Graylog is an open-source log management system. Graylog centrally captures, collects, enhances, stores, and analyzes log data. It is an affordable alternative to Splunk.
Below are a couple of steps to install Graylog on CentOS 7.
Edit interface, change ONBOOT from “no” to “yes”, and restart network service.
Step #1: Update your system and install needed packages.
hostnamectl set-hostname graylog
yum update -y
yum install epel-release
yum install pwgen vim


Step #2: Install JAVA
yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless.x86_64Check the java version.
java -version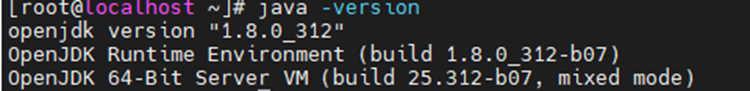
Create a repository file. Then add the content below to this repository.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org.repo
--
[mongodb-org-4.2]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.2/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.asc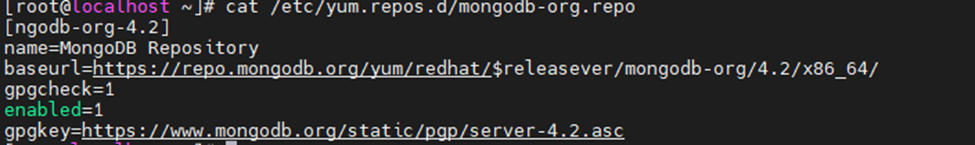
Install MongoDB
yum install mongodb-org
Enable and start mongoDB service on system.
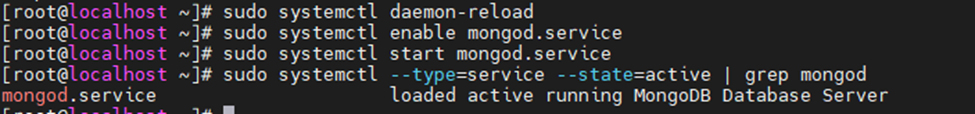
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable mongod.service
sudo systemctl start mongod.service
sudo systemctl --type=service --state=active | grep mongod
Check MongoDB service port.
netstat -antp | grep 27017
Step #4: Installing Elasticsearch
Graylog can be used with Elasticsearch 6x, 7.x, In this lab, I have used version 6x of Elasticsearch.
Install the Elastic GPG key.
rpm –import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch

Create a repository, then add the following contents to the file.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo
[elasticsearch-6.x]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-6.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md
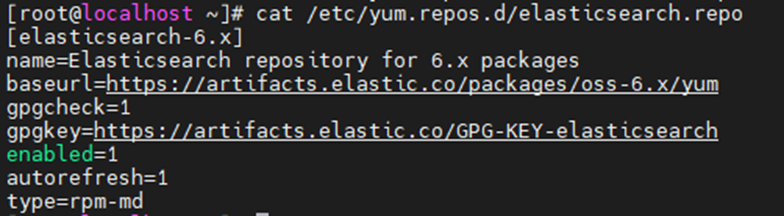
Install the open-source version of Elasticsearch.
yum install elasticsearch-ossModify the Elasticsearch configuration file. Set the cluster name to graylog and add “action.auto_create_index: false” to the file.
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
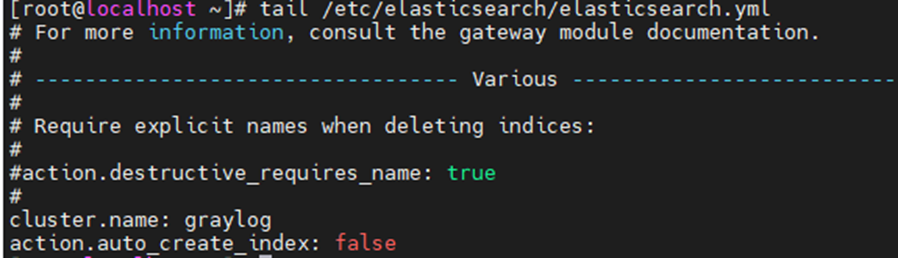
Save and exit the file.
Enable, start and check the status of elastic search on the system.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
sudo systemctl --type=service --state=active | grep elasticsearchCheck elastic search health.
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true'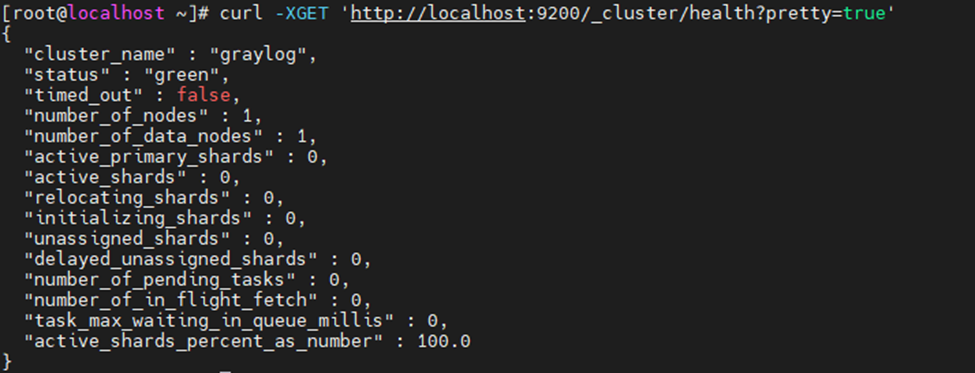
Step #5: Installing the Graylog
Now install the Graylog repository configuration with the following commands:
rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-4.2-repository_latest.rpmInstall Graylog-server.
yum install graylog-server
Configure Graylog:
Add “password_secret” and “root_password_sha2” to server.conf file.
Generate password_secret.
pwgen -N 1 -s 96

Generate root_password_sha2.
echo -n foss@dan123 | sha256sum | cut -d” ” -f1

Edit etc/graylog/server/server.conf file.
vim /etc/graylog/server/server.conf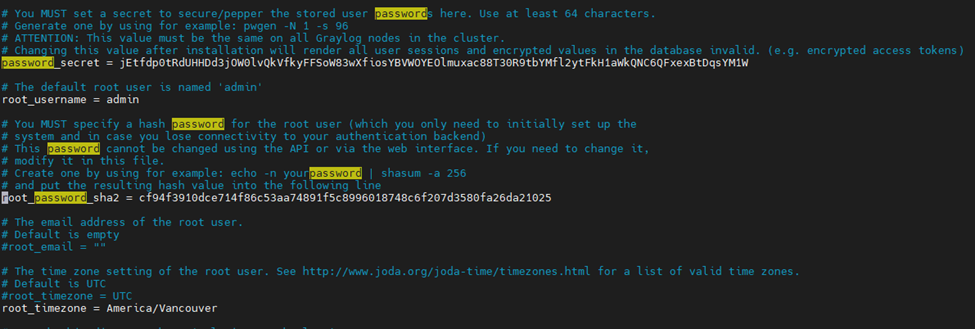
Uncomment the following line.
http_bind_address = 127.0.0.1:9000
and add http_bind_address = 10.0.0.33:9000
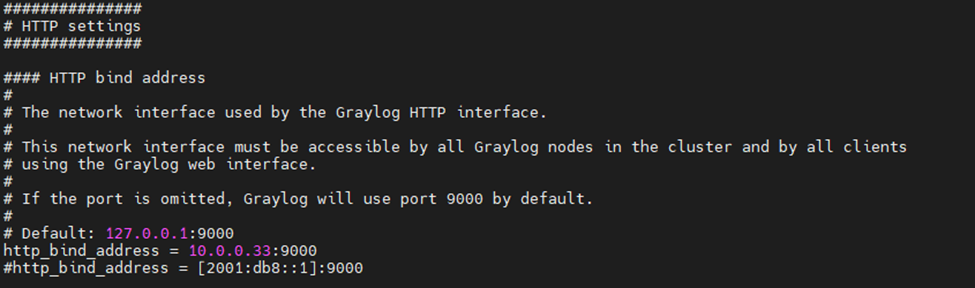
Enable and Start service.
systemctl enable graylog-server.service
systemctl start graylog-server.serviceMonitor server logs.
tail -f /var/log/graylog-server/server.log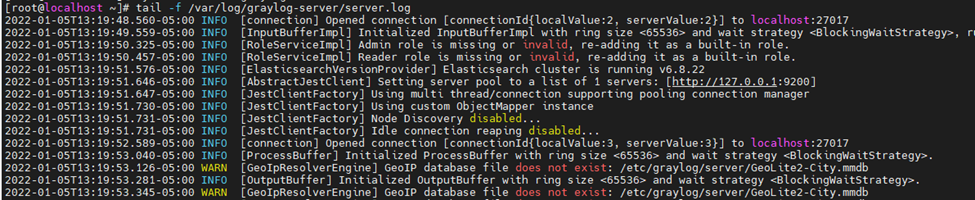
Copy Geo-IP database to Graylog server.
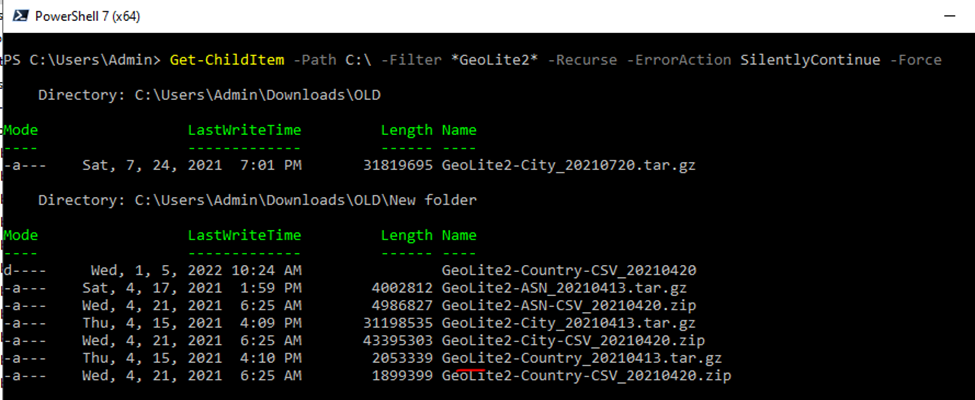

Check log again.
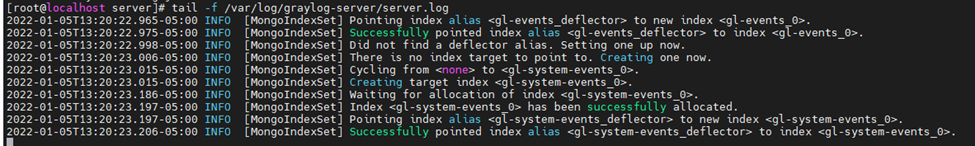
Check Graylog Server listening port.
netstat -antp | grep 9000
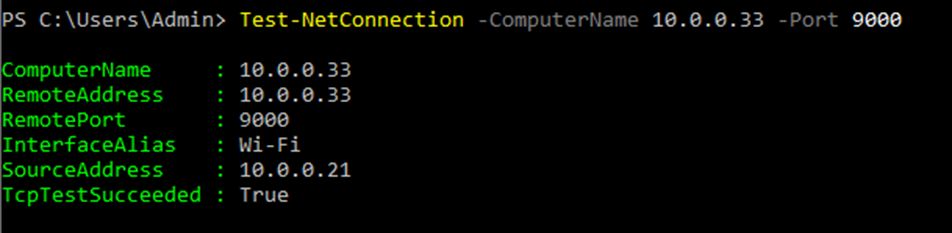
Check the port is opened on a remote host.
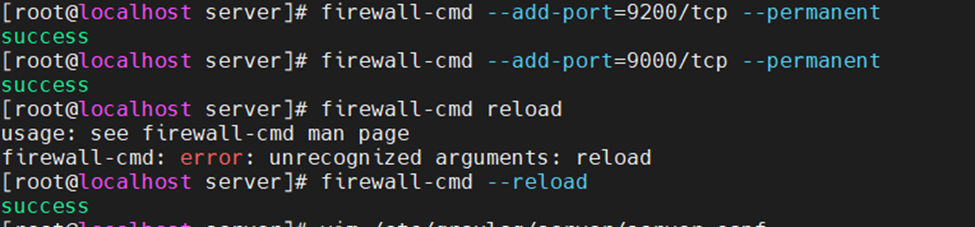
Allow Graylog service on Firewall.
Access Graylog web interface on another machine.