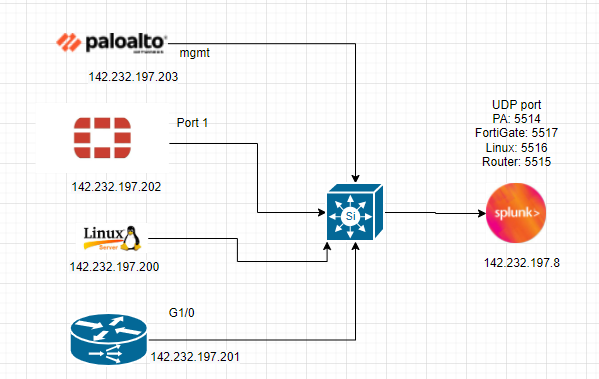
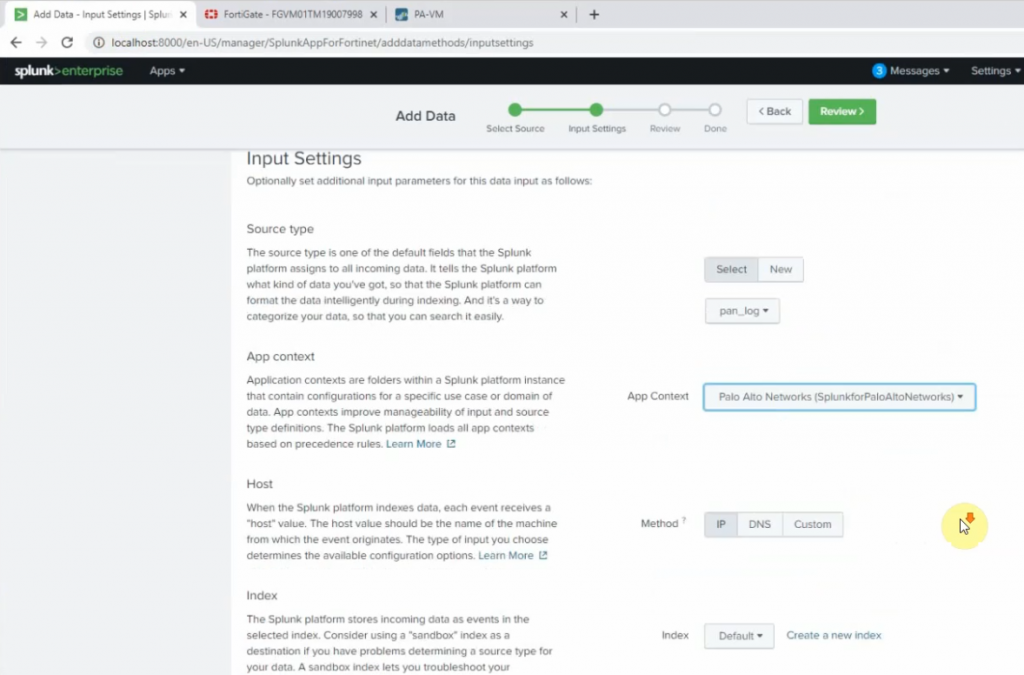
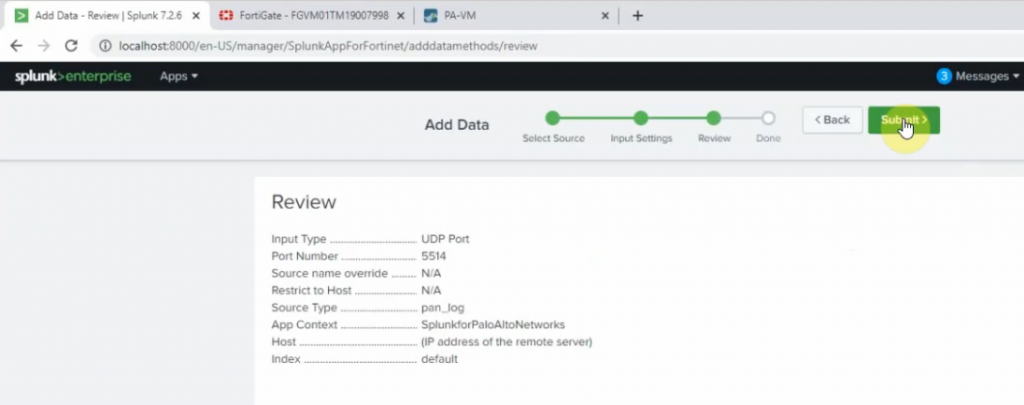
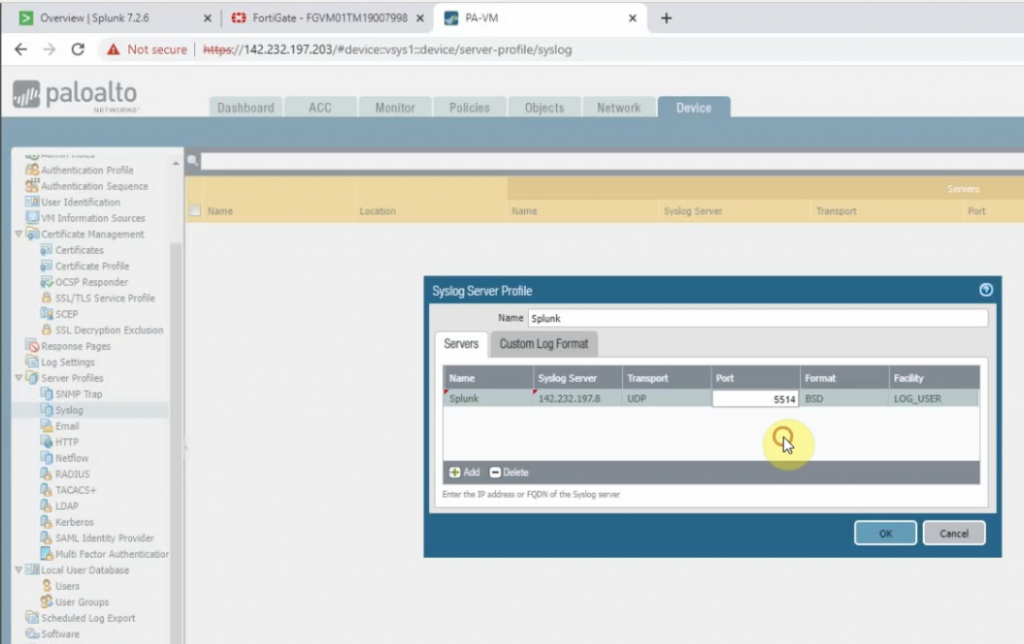
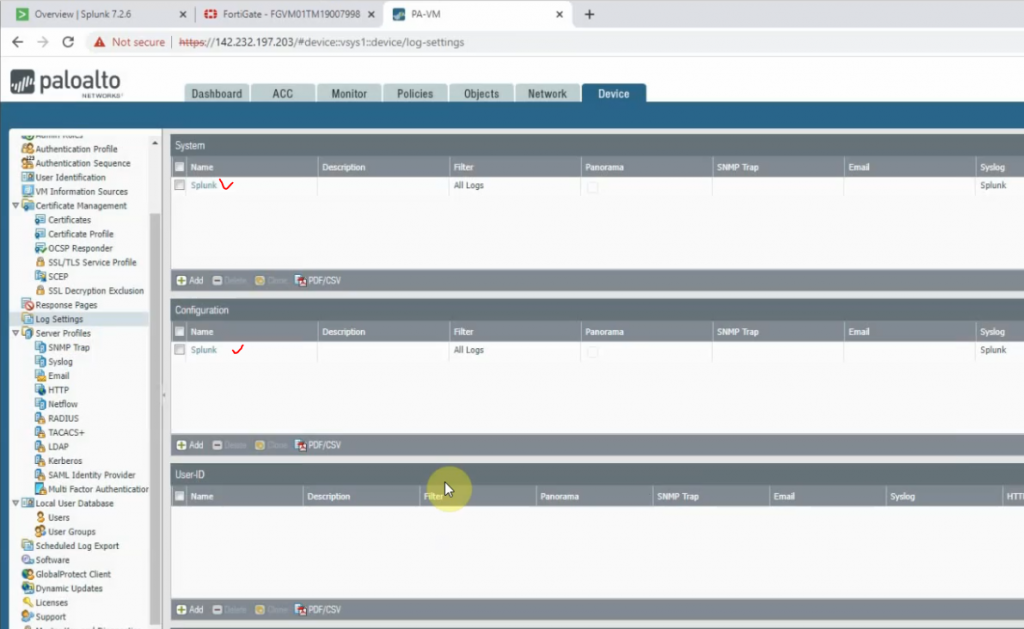
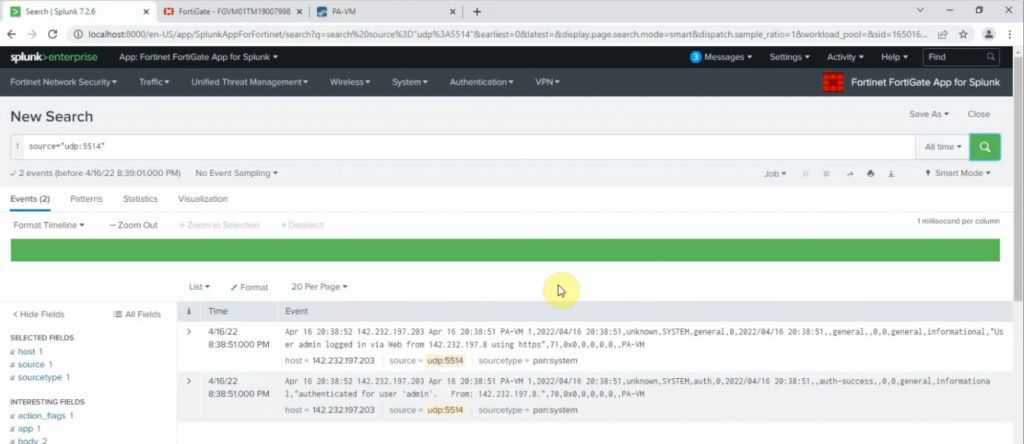
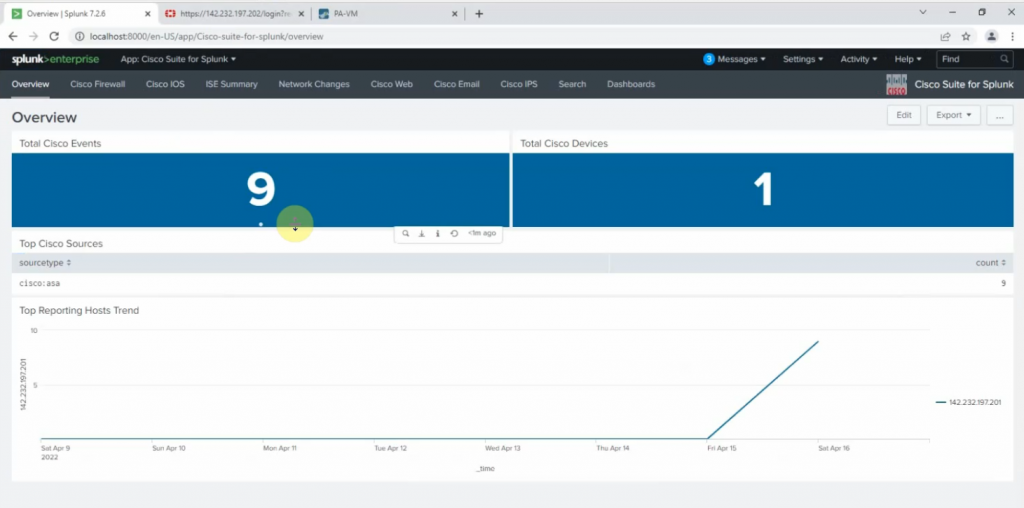
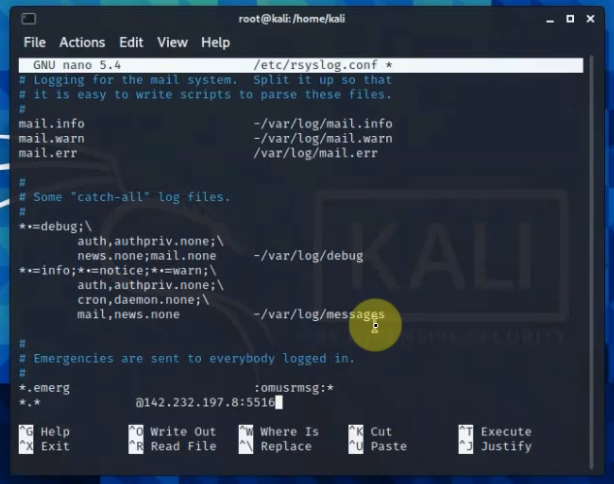
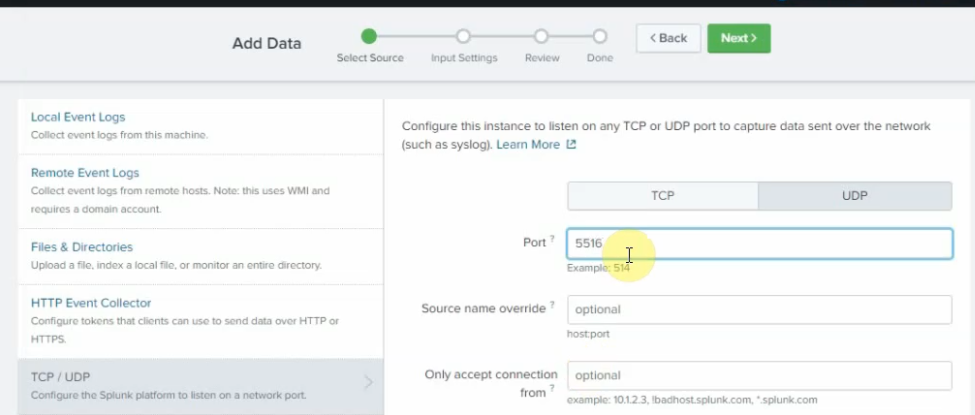
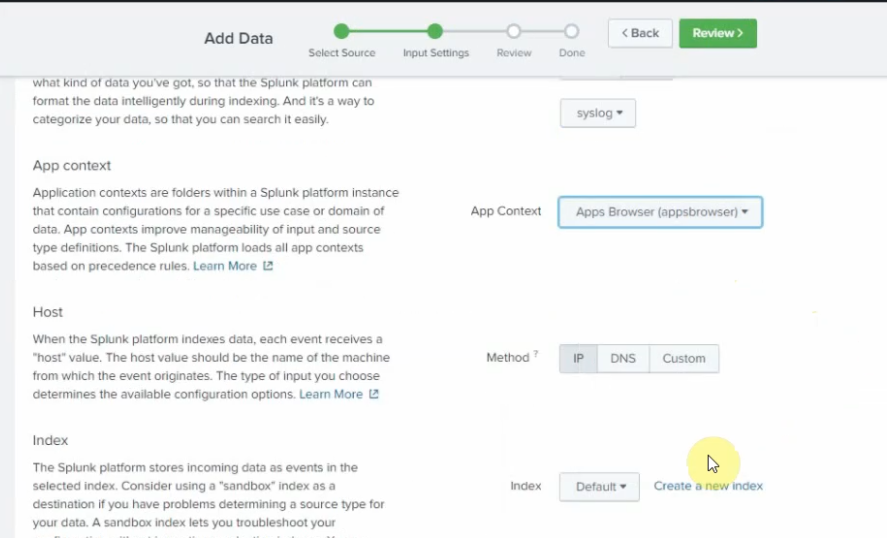
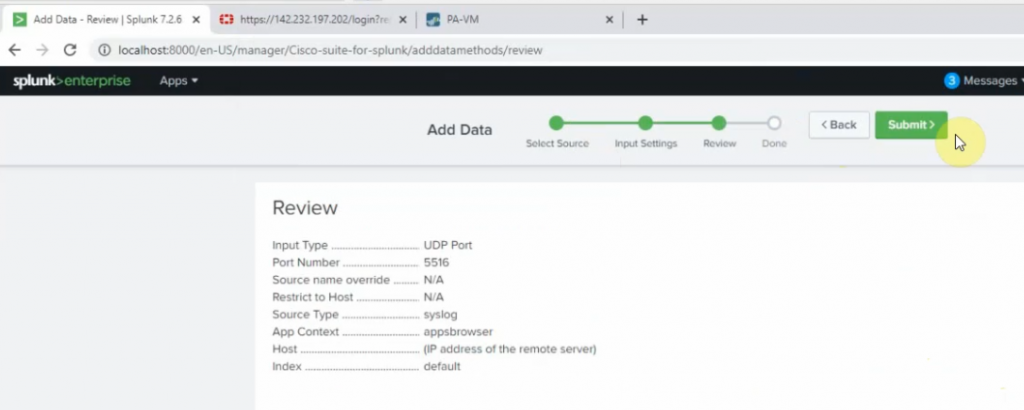
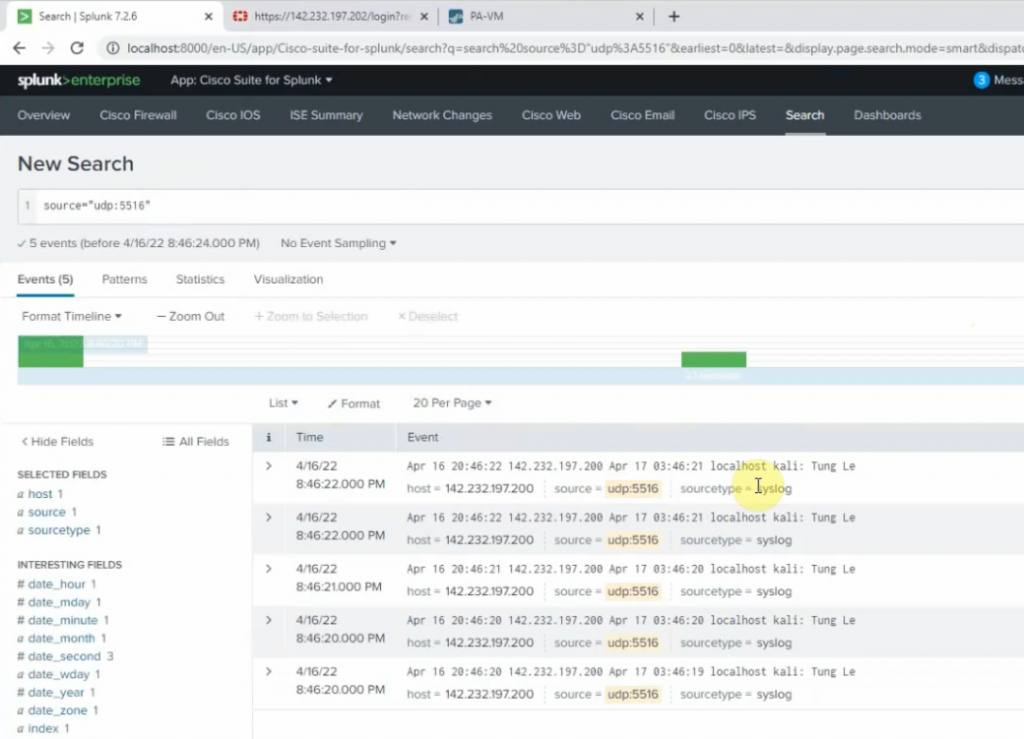
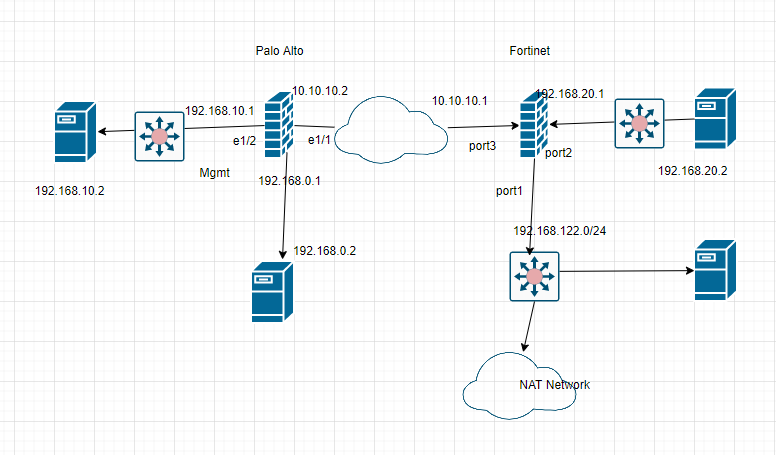
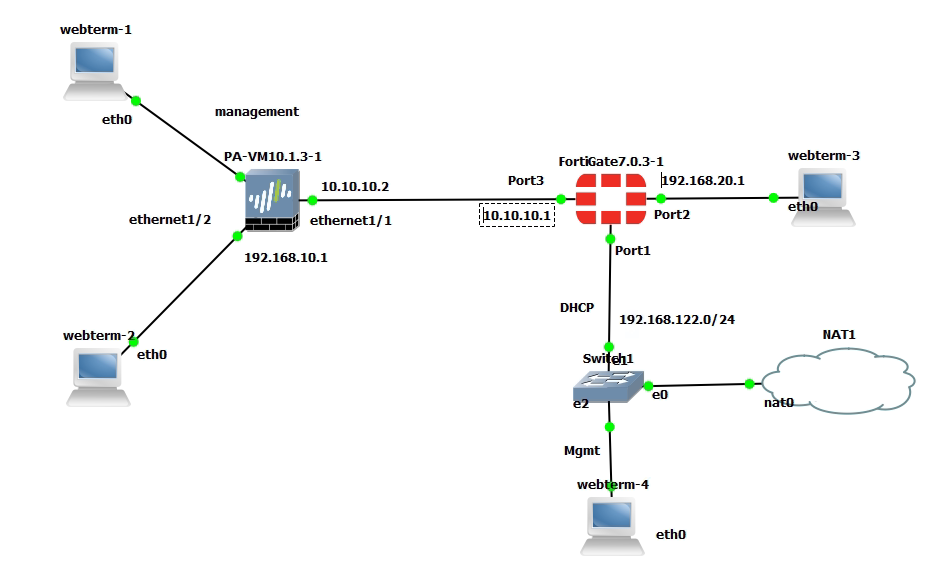
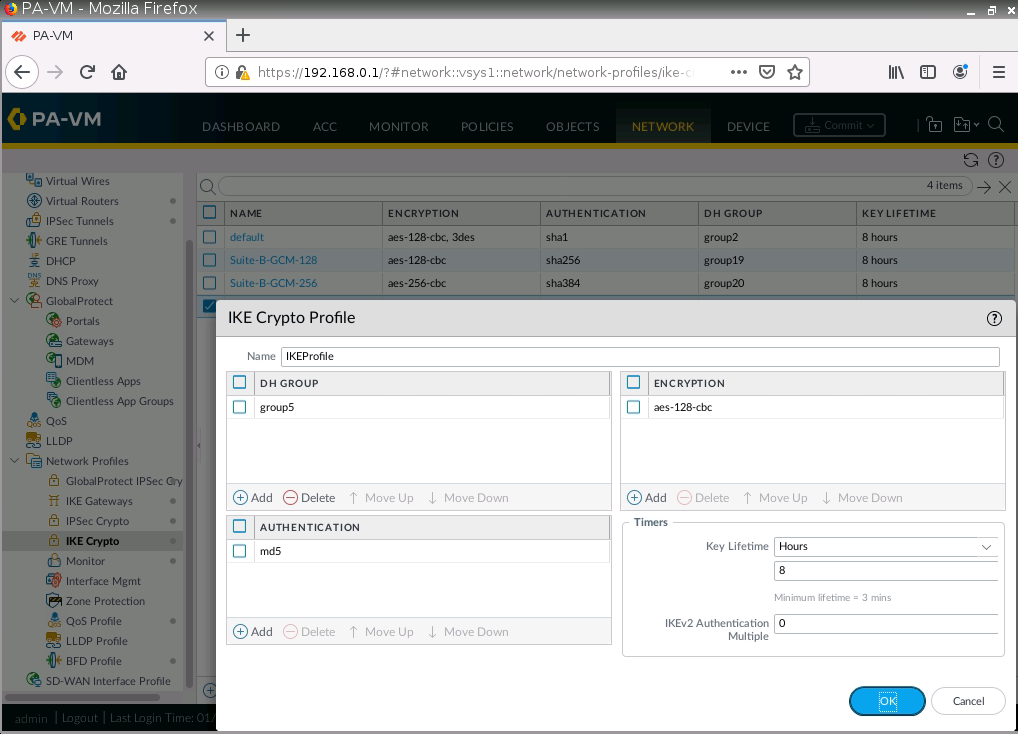
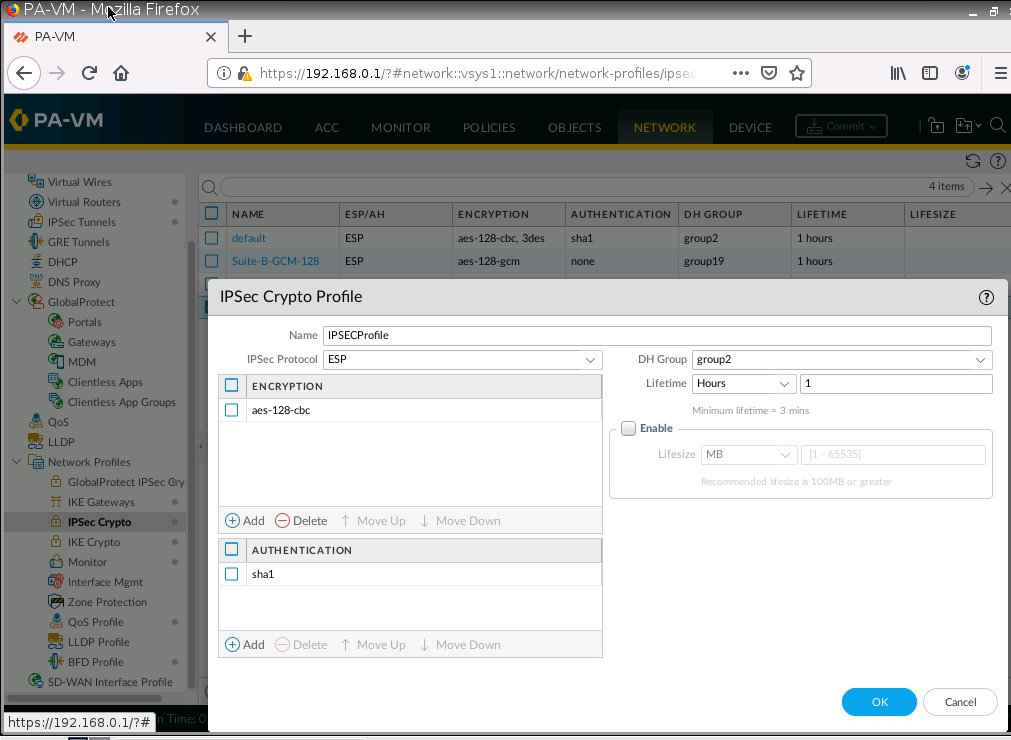
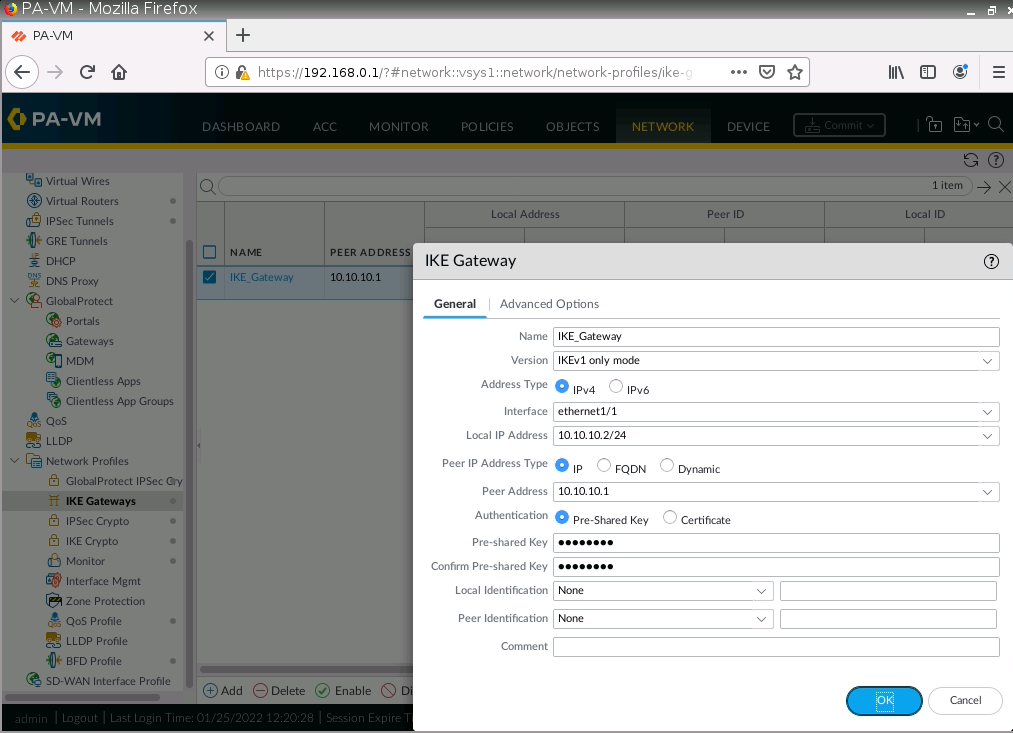
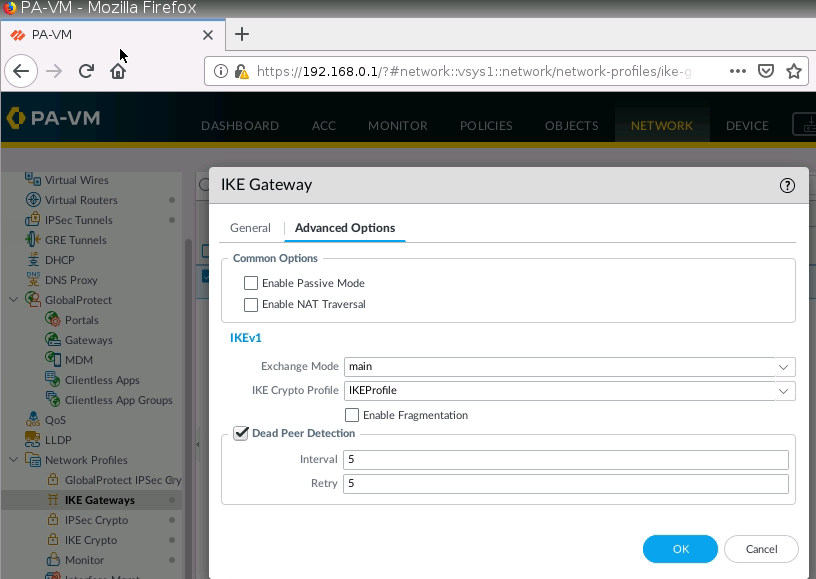
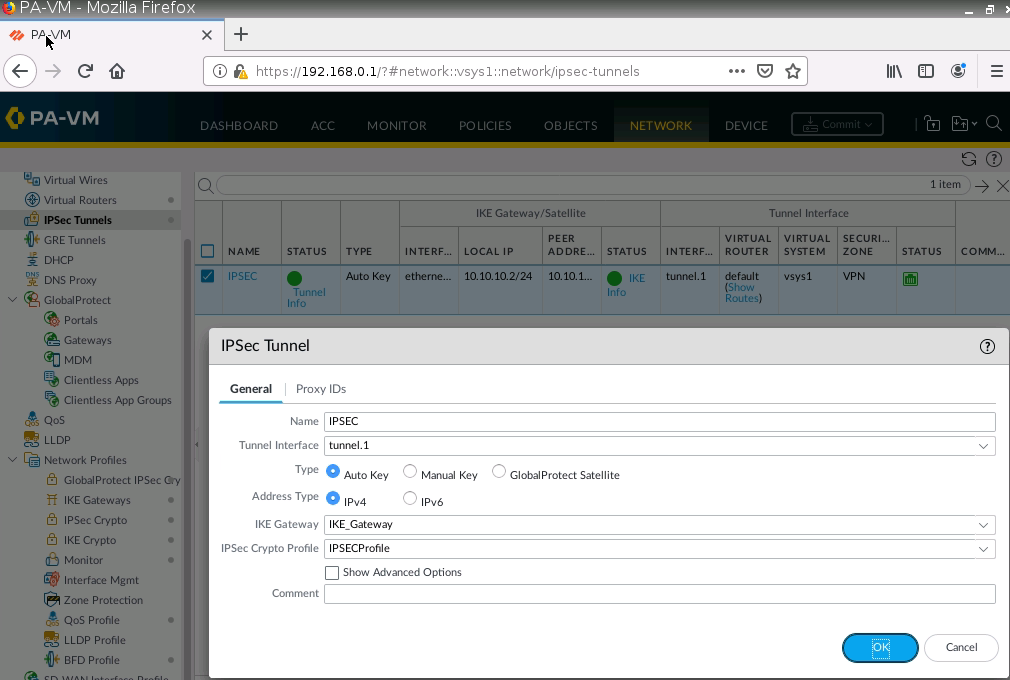
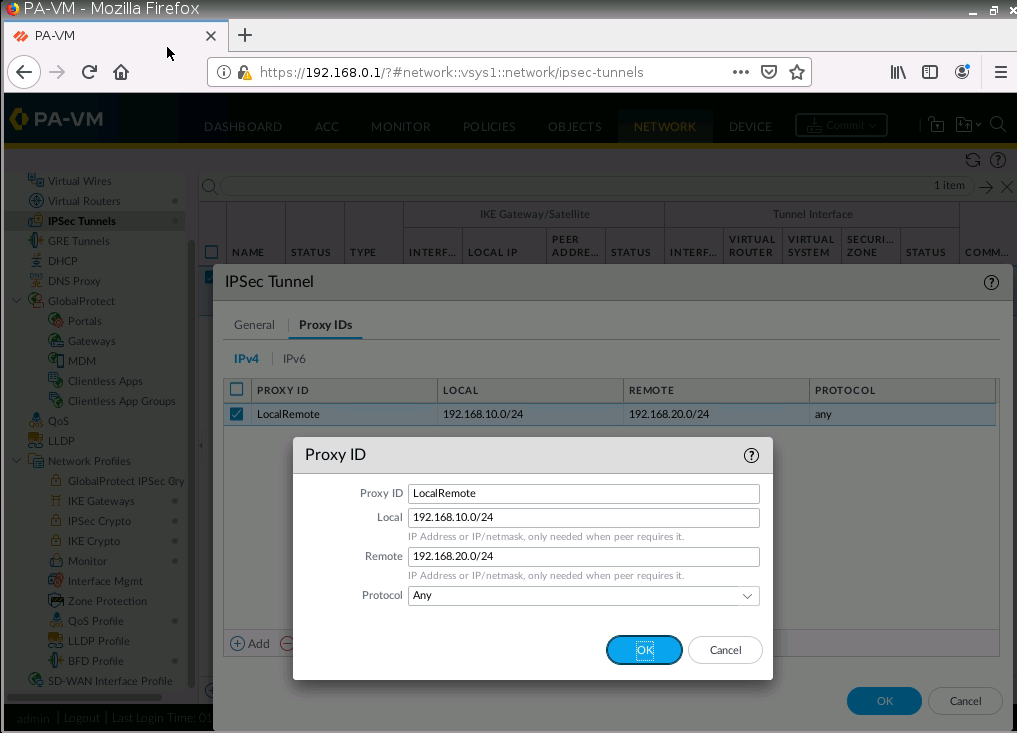
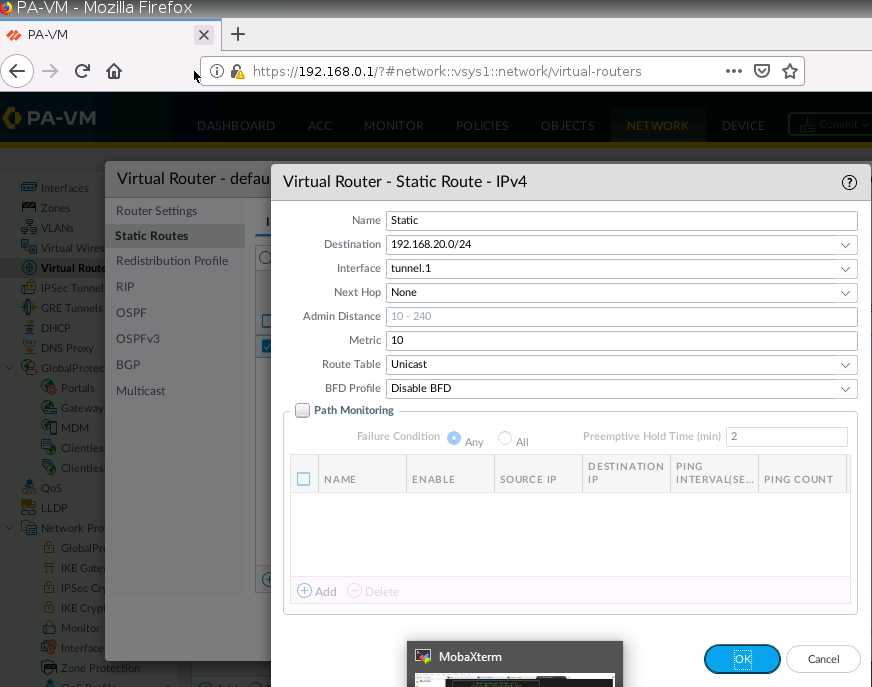
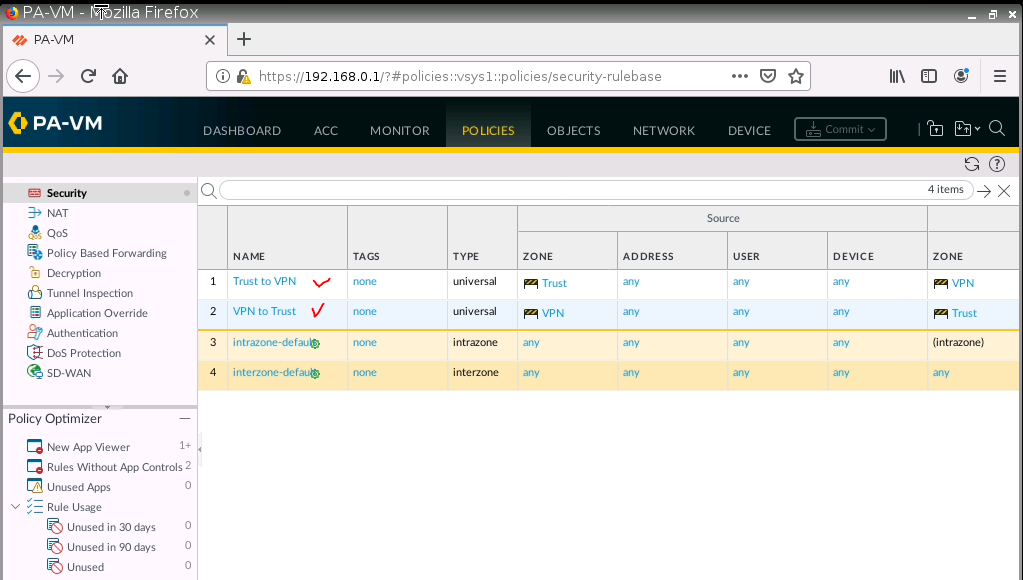
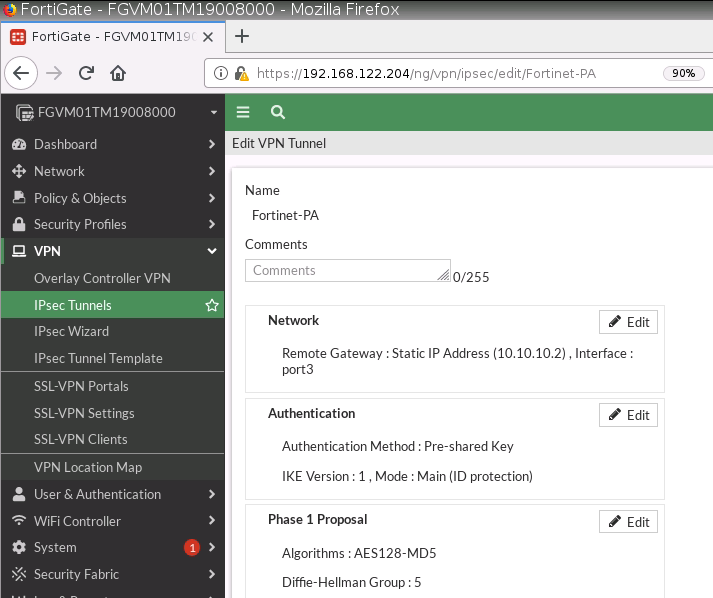
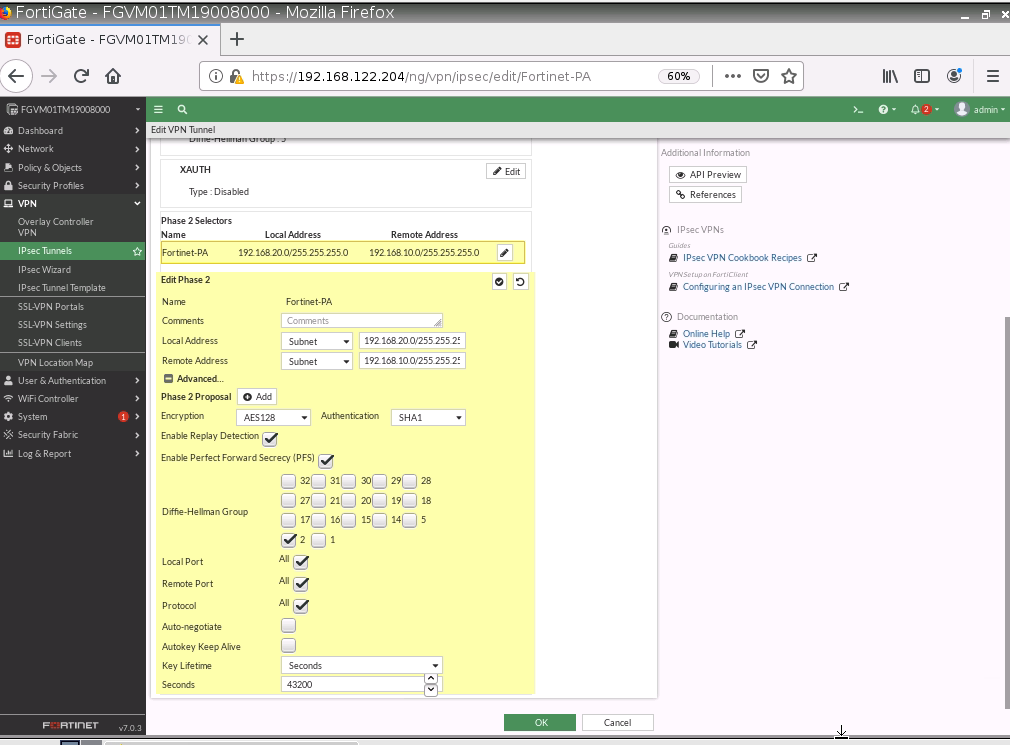
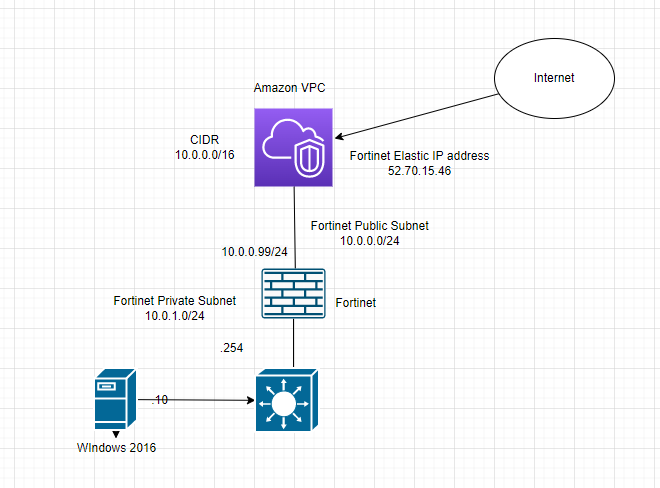
Diagram.
Below are a couple of steps to deploy Fortinet on AWS.
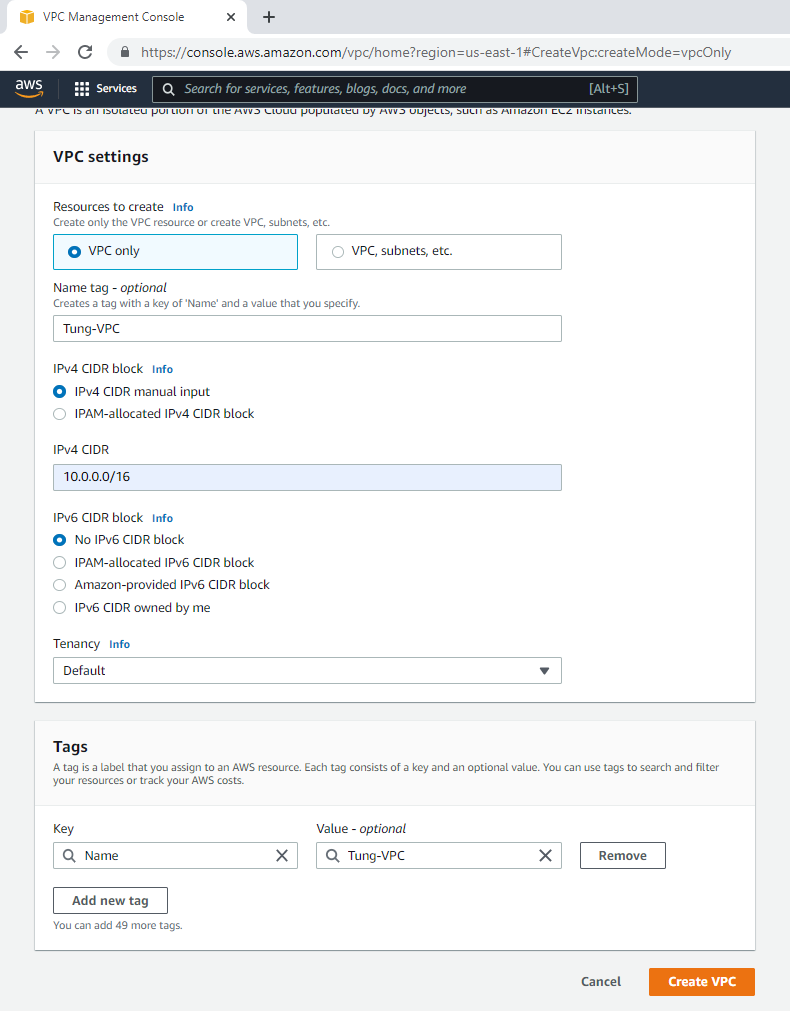
Create a new VPC.
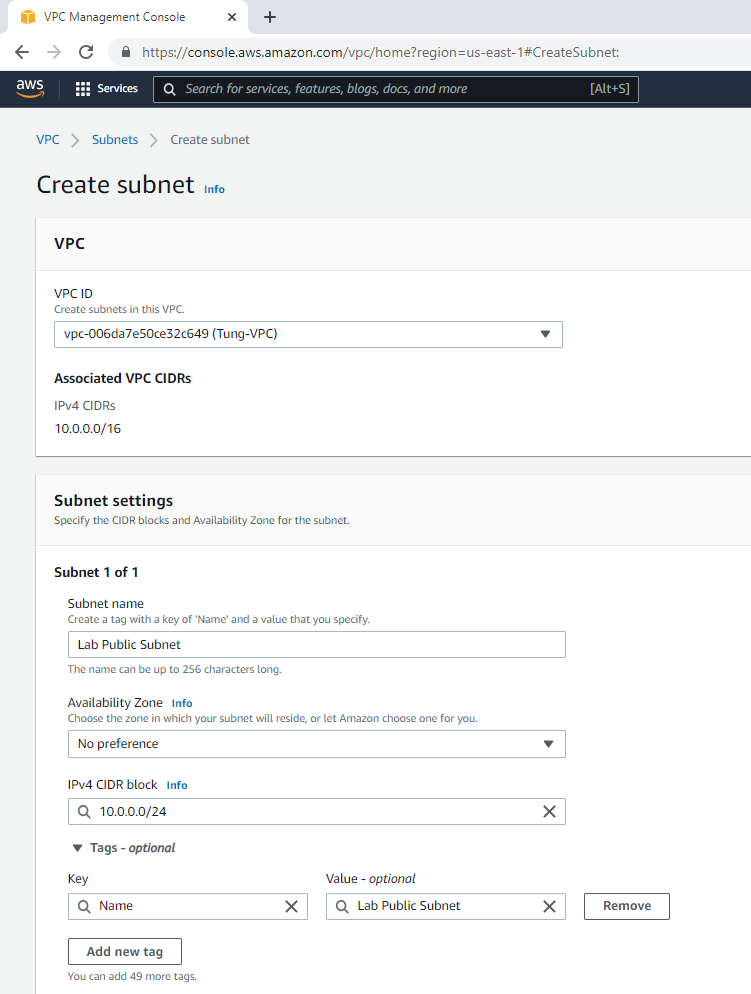
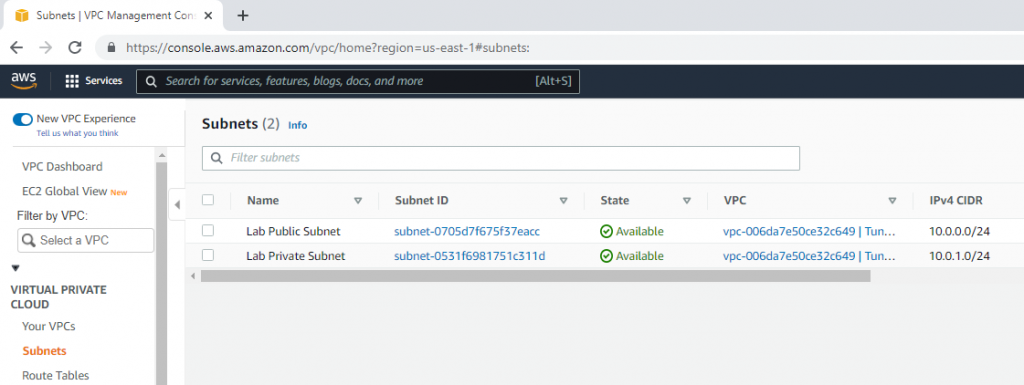
Create a public subnet.
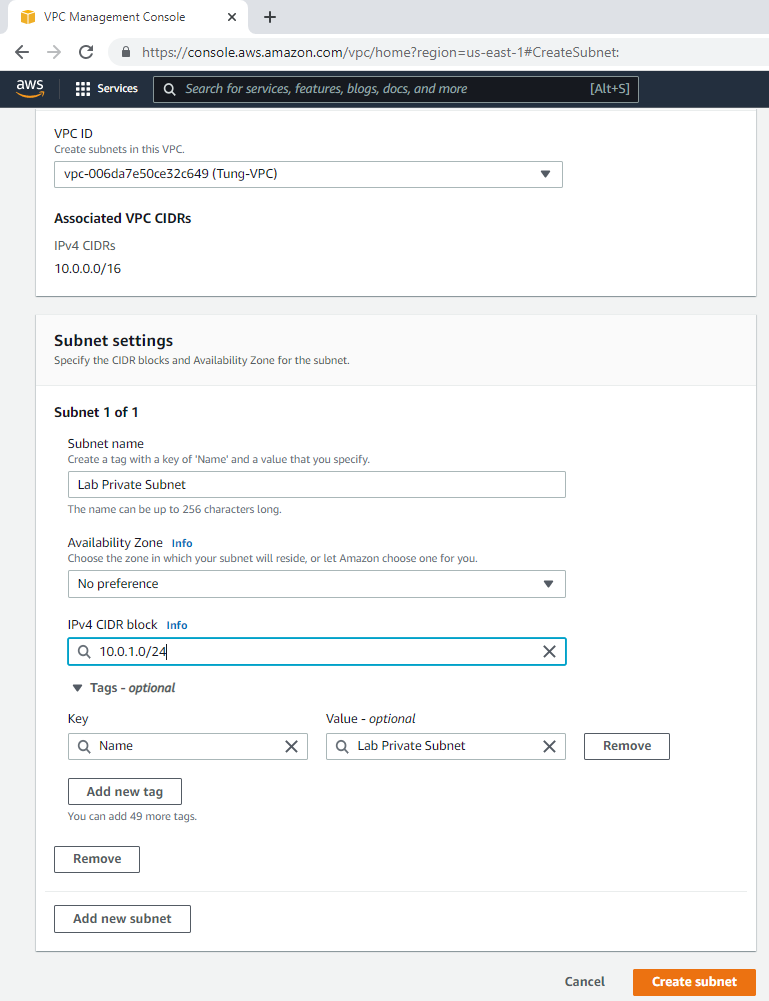
Create a private subnet.
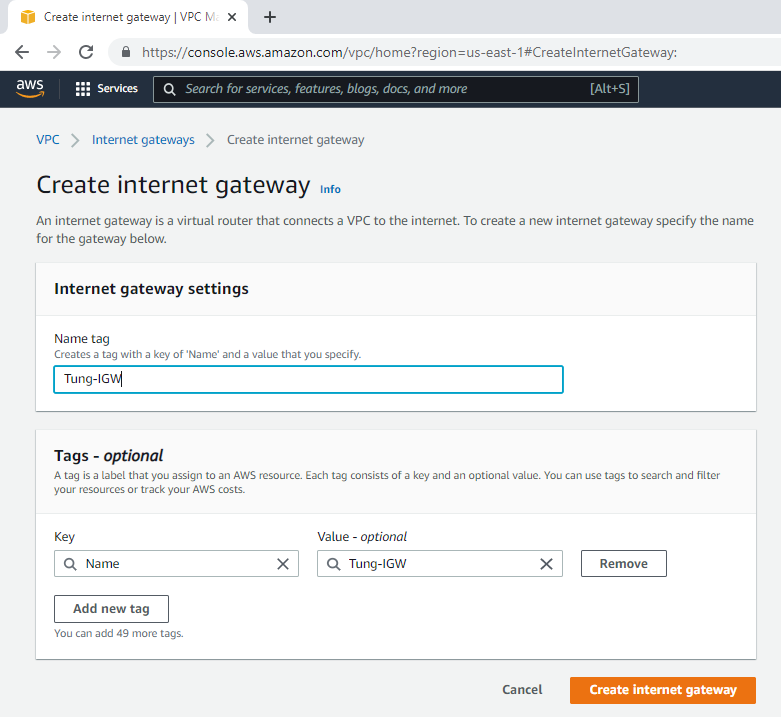
Create an Internet gateway.
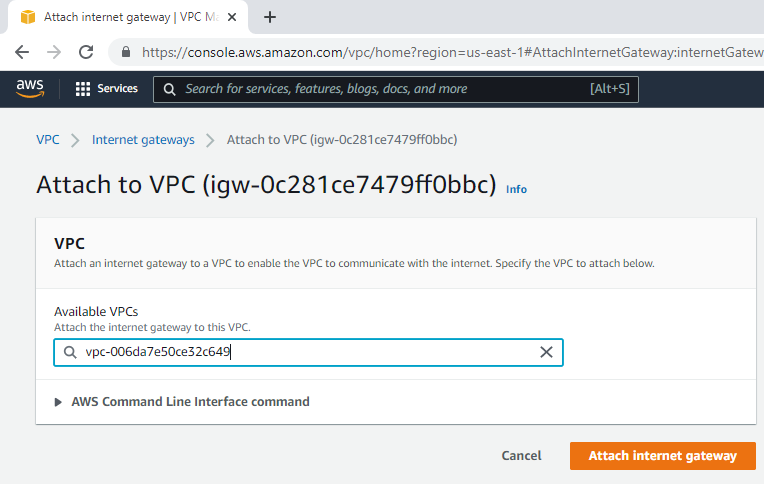
Attach the gateway to your VPC.
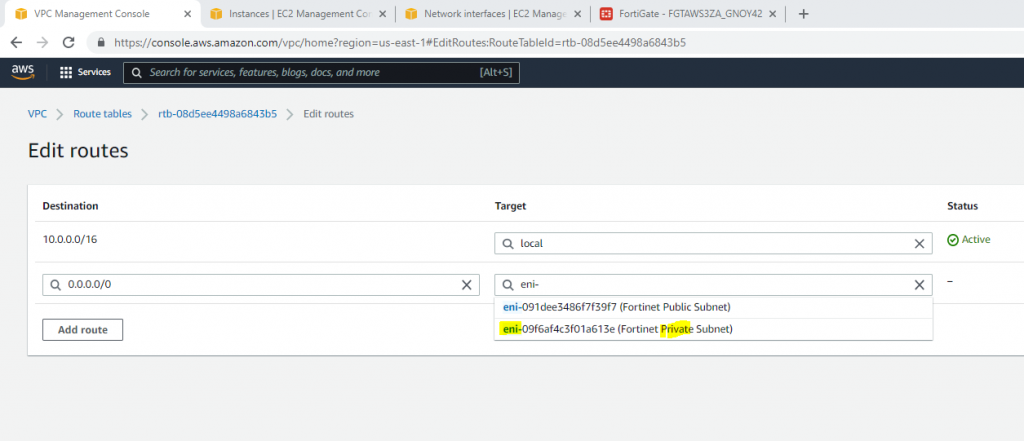
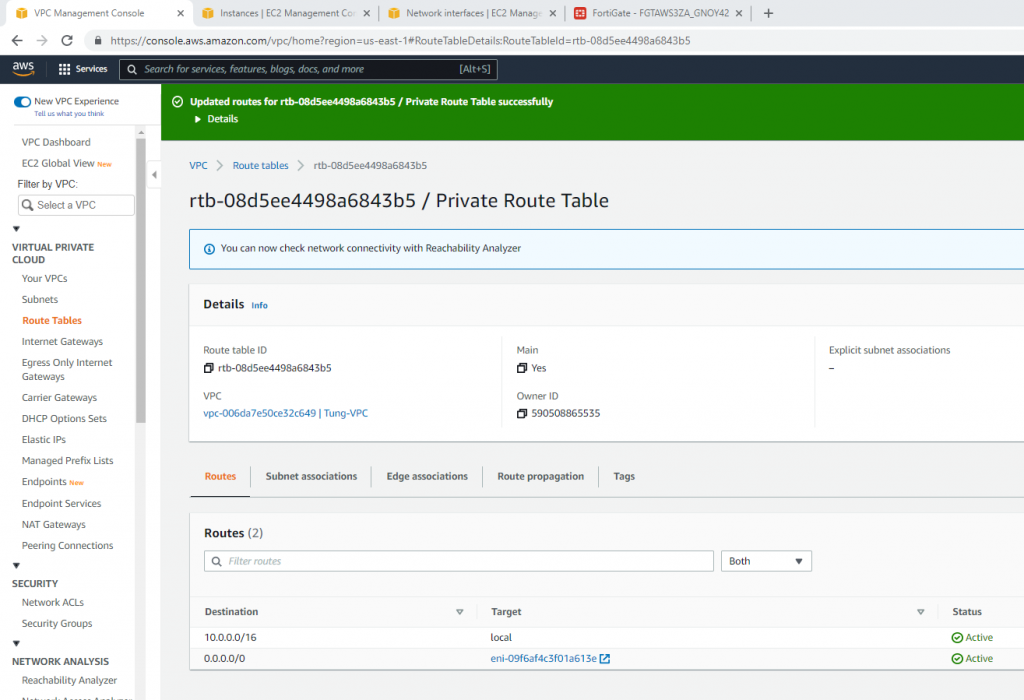
Edit Route table, change default Route table to Private Route Table.
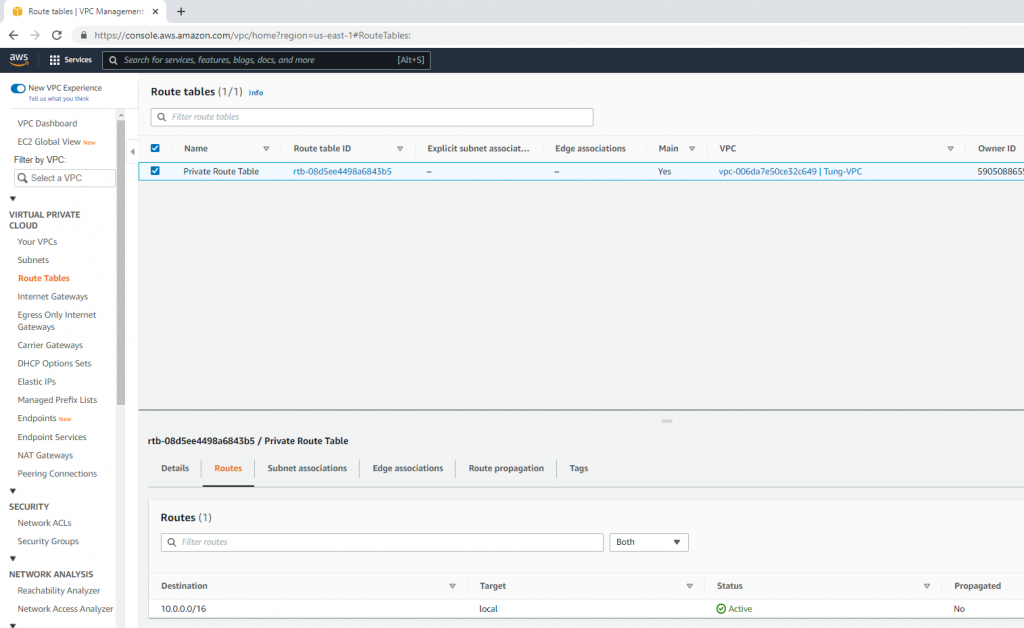
Create a Public Route Table.
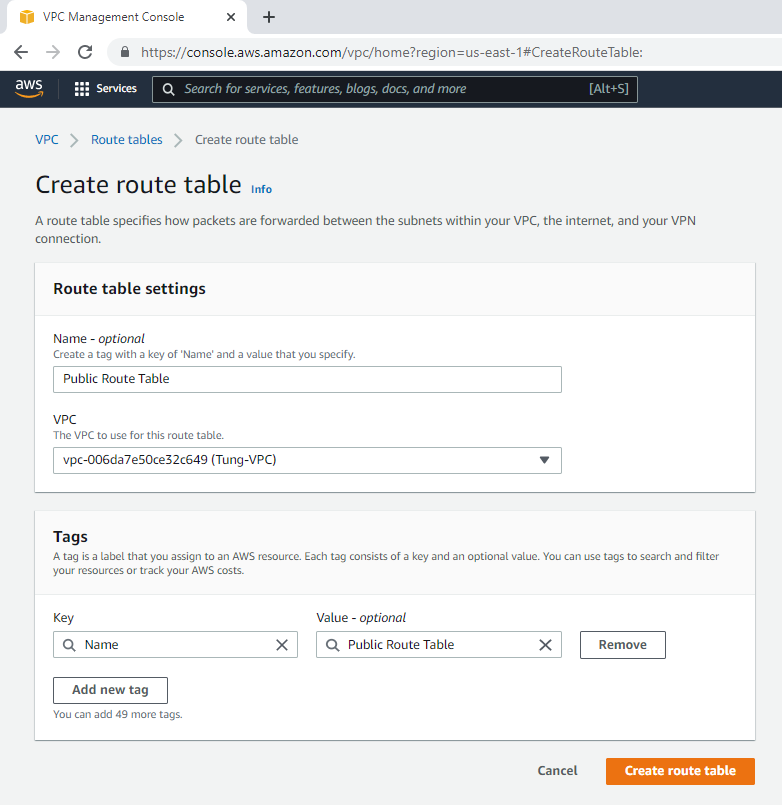
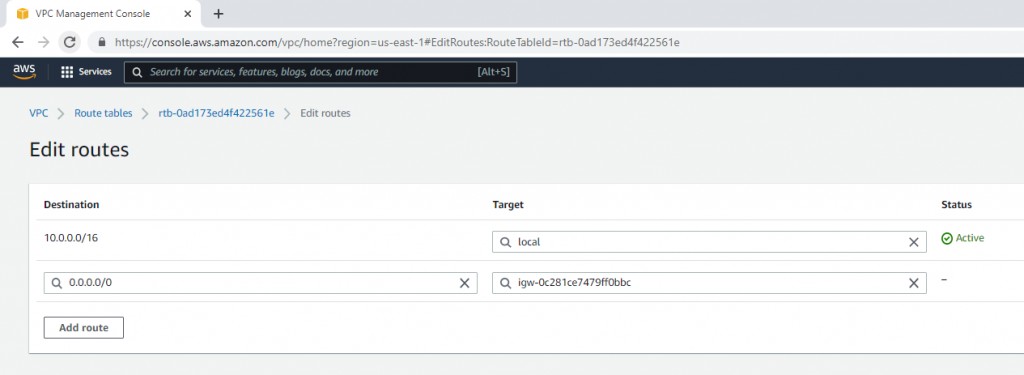
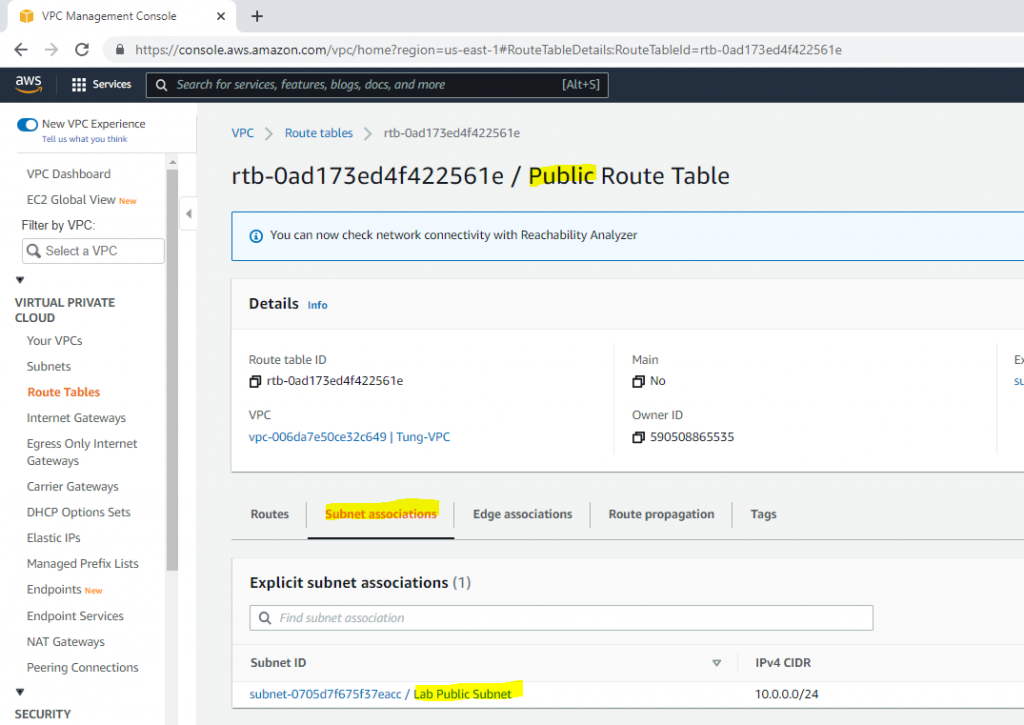
Link Lab Public Subnet to Public Route Table.
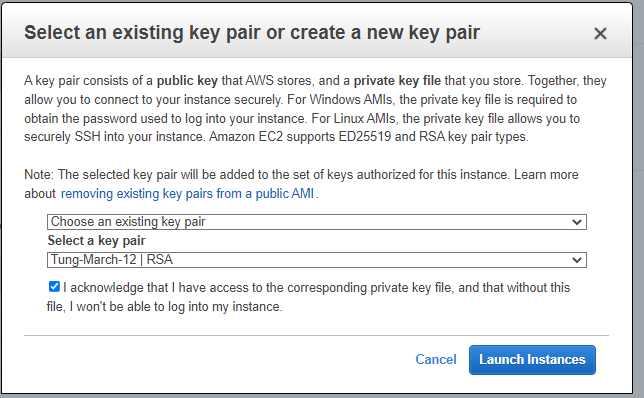
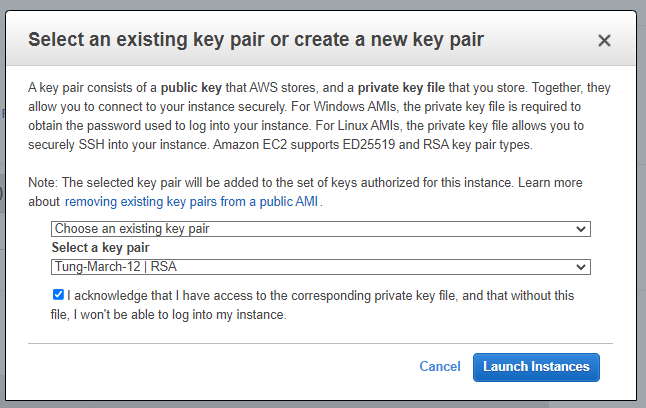
Create a new key pair.
Go to EC2, and deploy Fortinet on AWS.
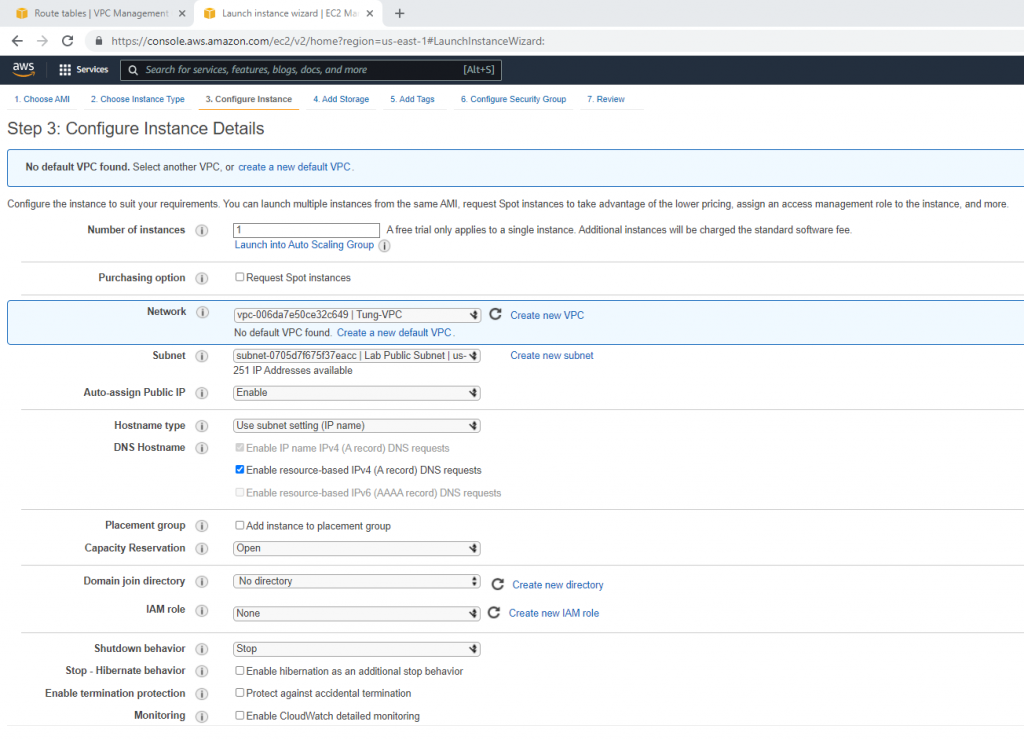
Select your VPC, the subnet belongs to Lab Public Subnet. Also Auto-assign Public IP is Enable.
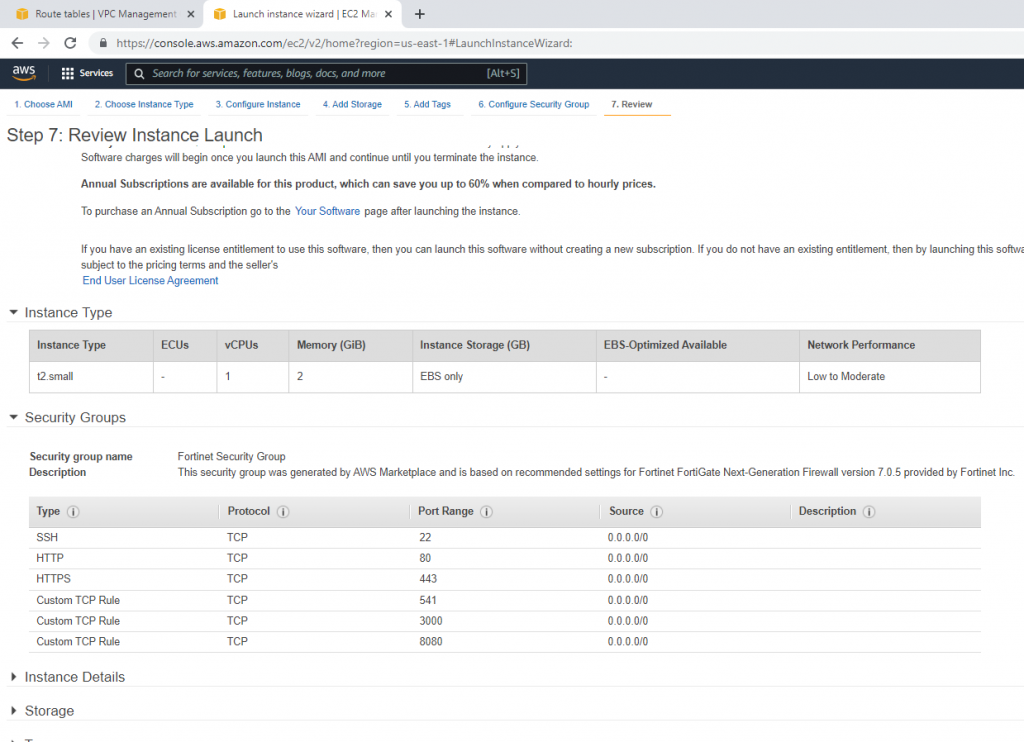
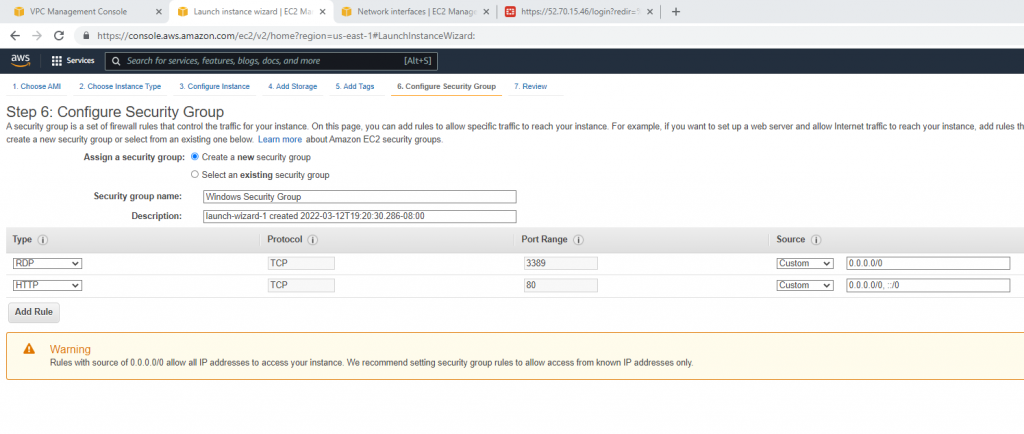
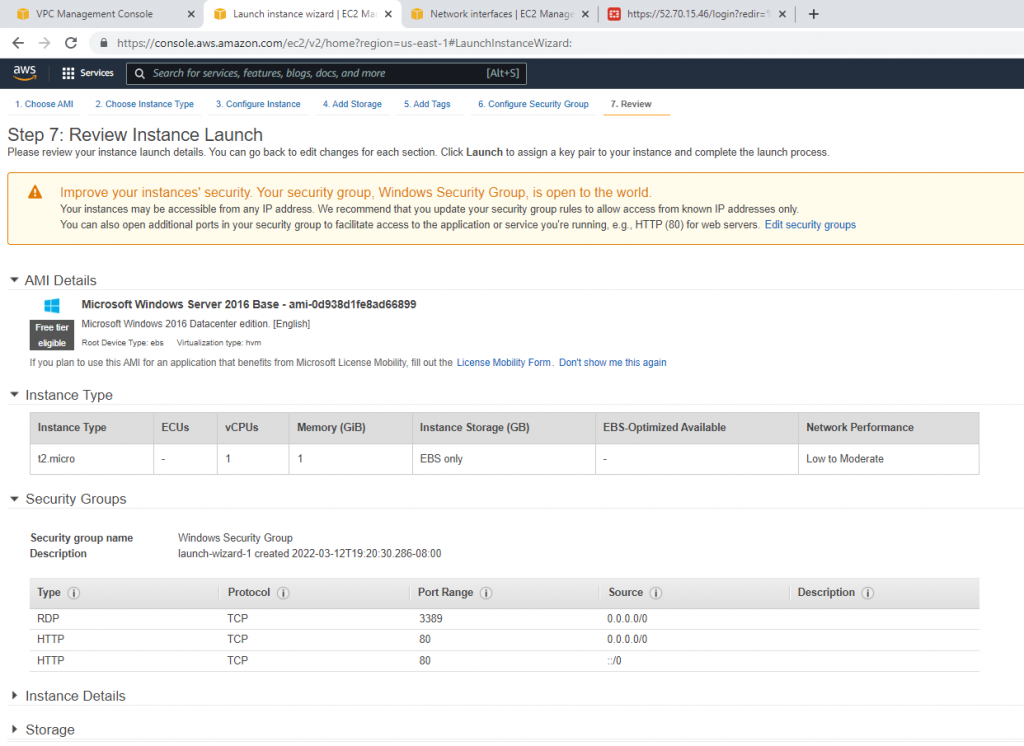
Security Group.
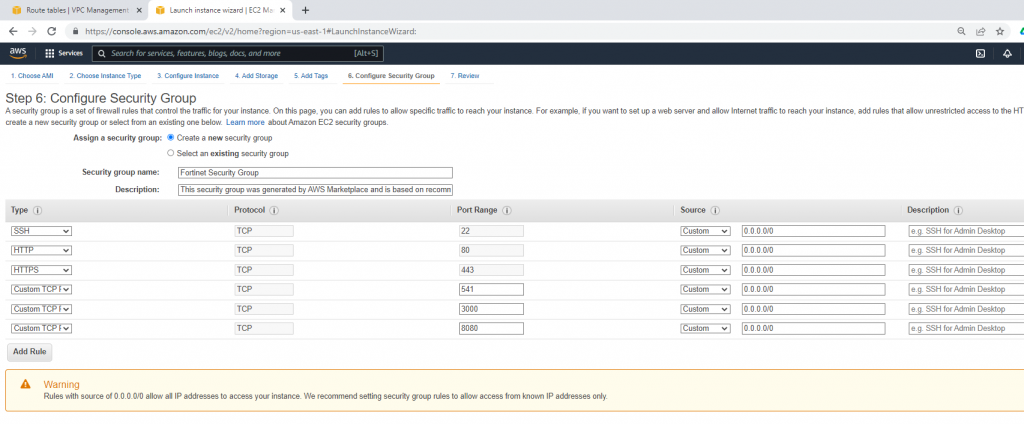
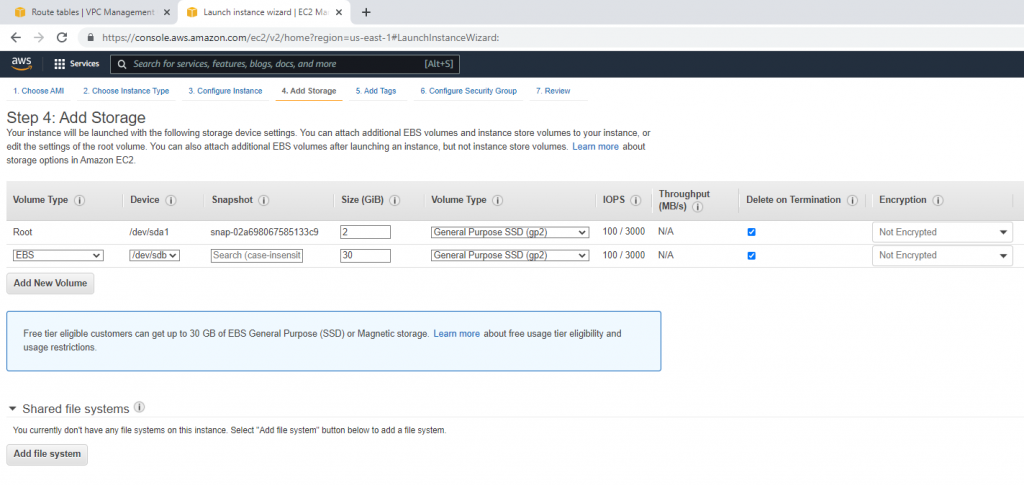
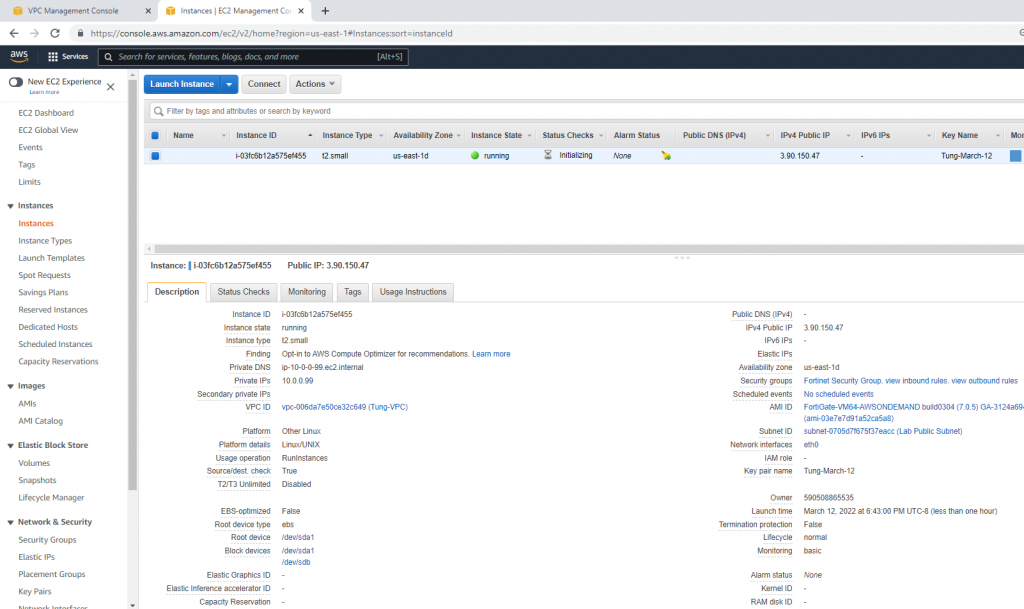
Go to Network interfaces. Change the interface to Fortinet Public Subnet.
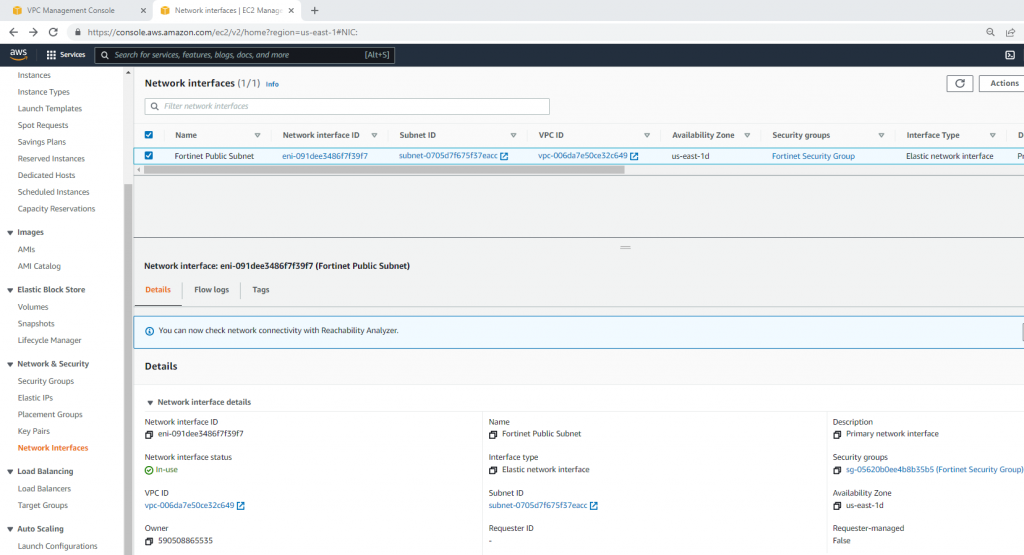
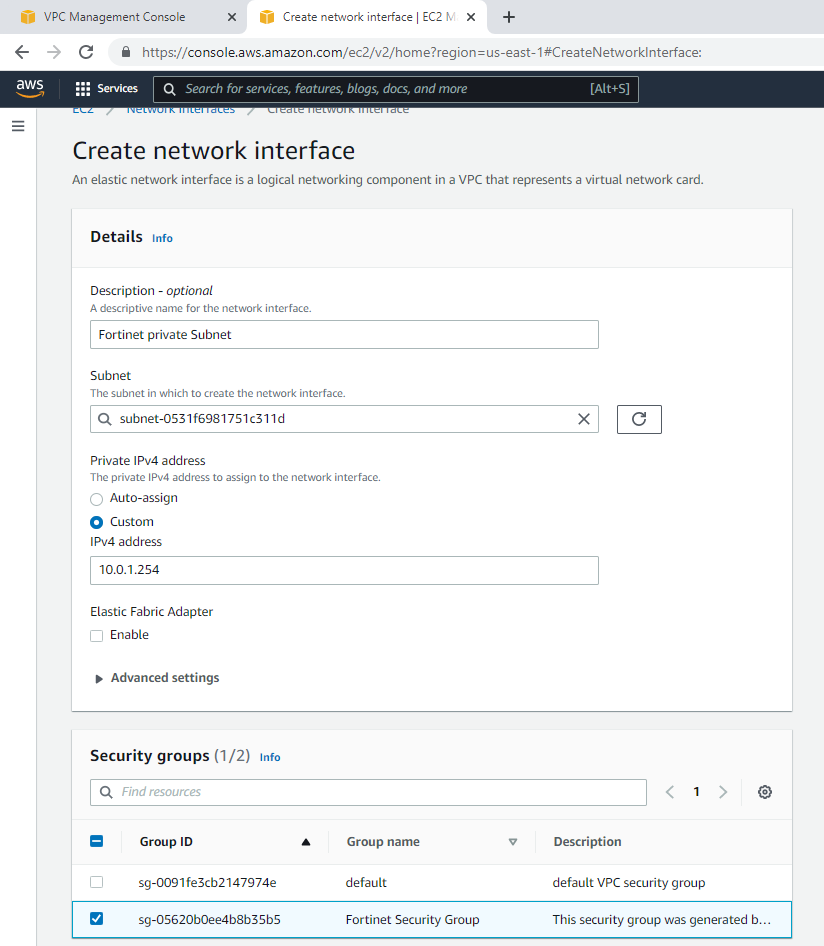
Create a new Fortinet Private subnet.
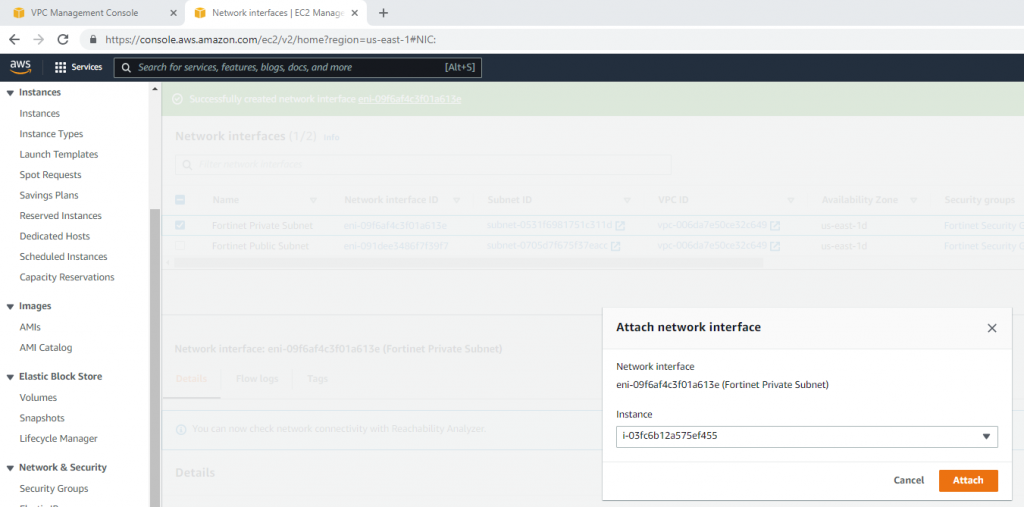
Attach this network interface to Fortinet EC2.
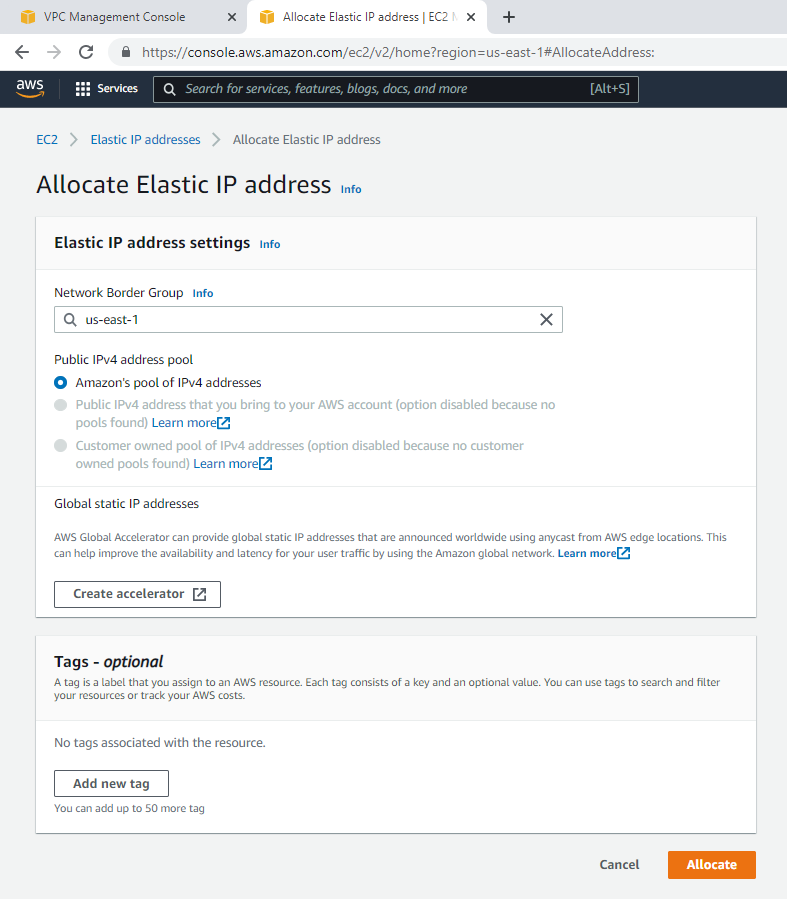
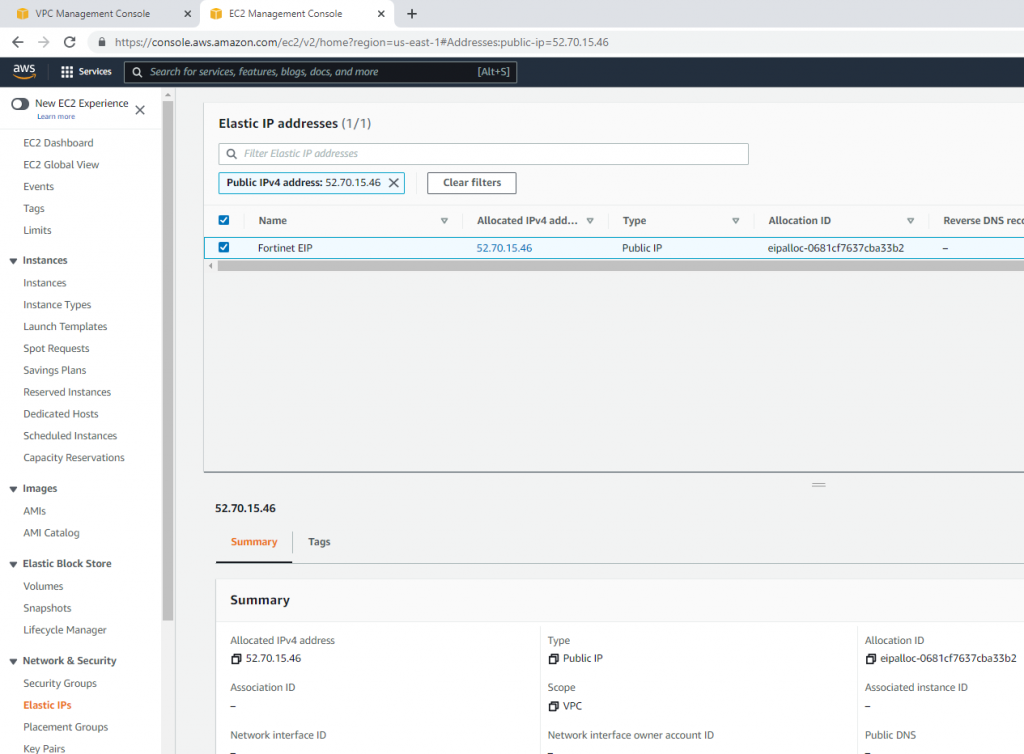
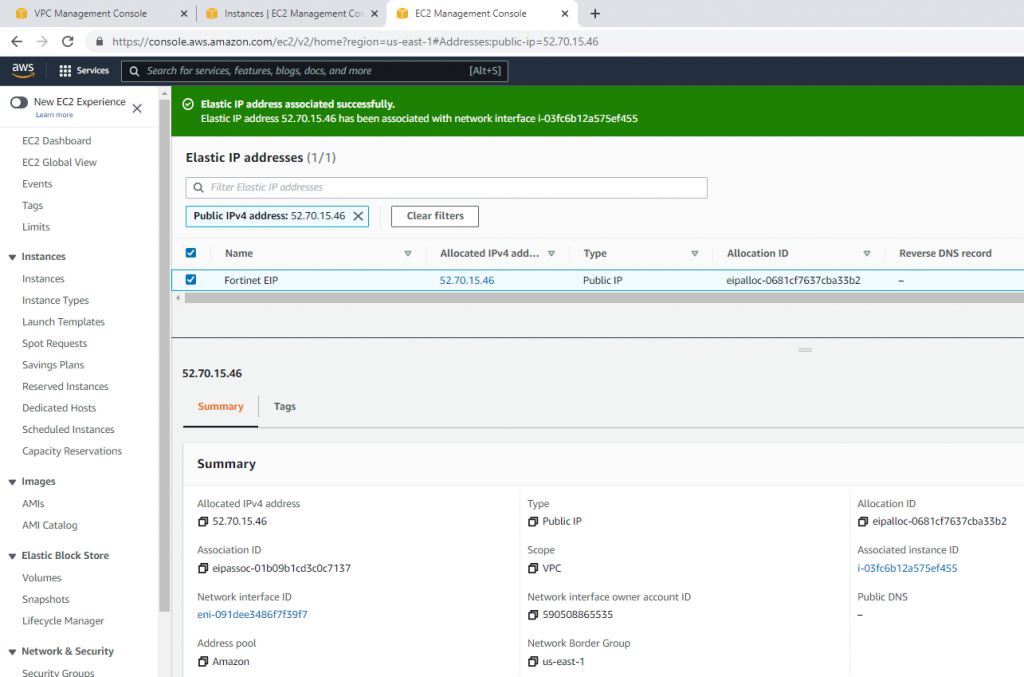
Create a new Elastic IP address.
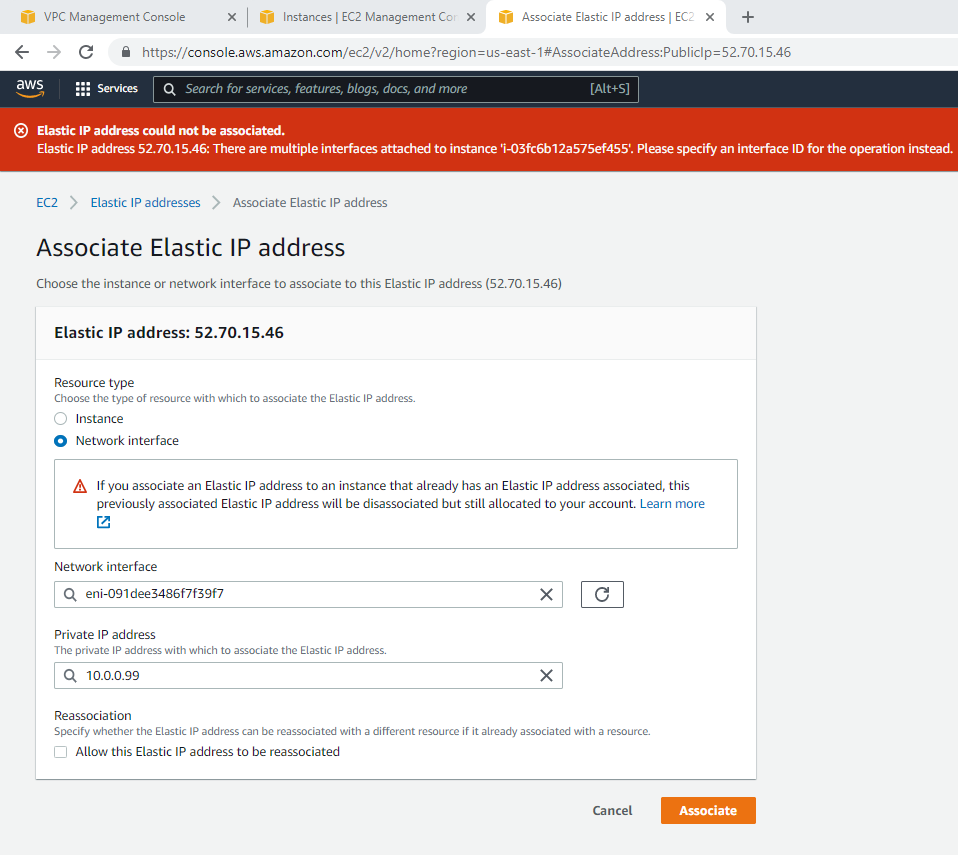
Associate this Elastic IP address to Fortinet EC2.
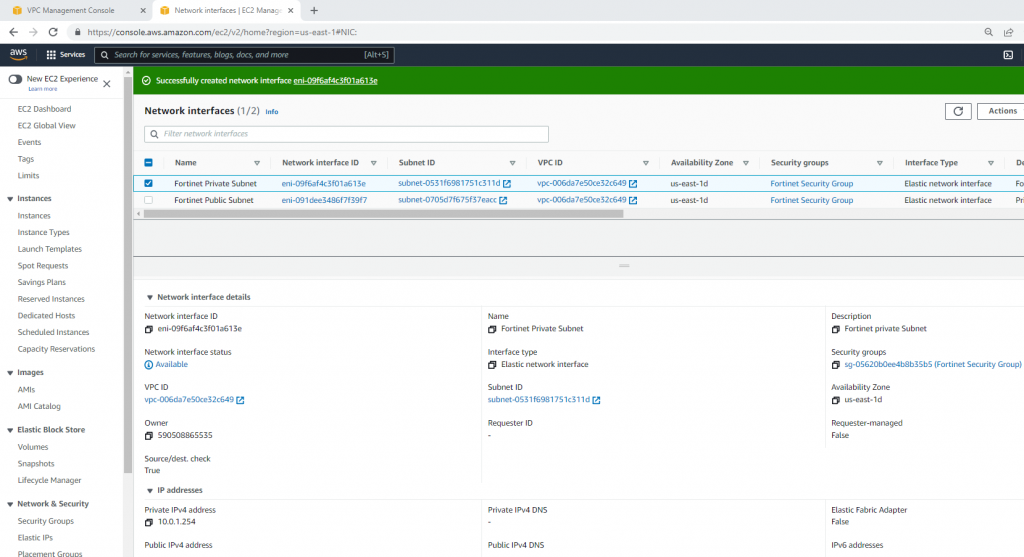
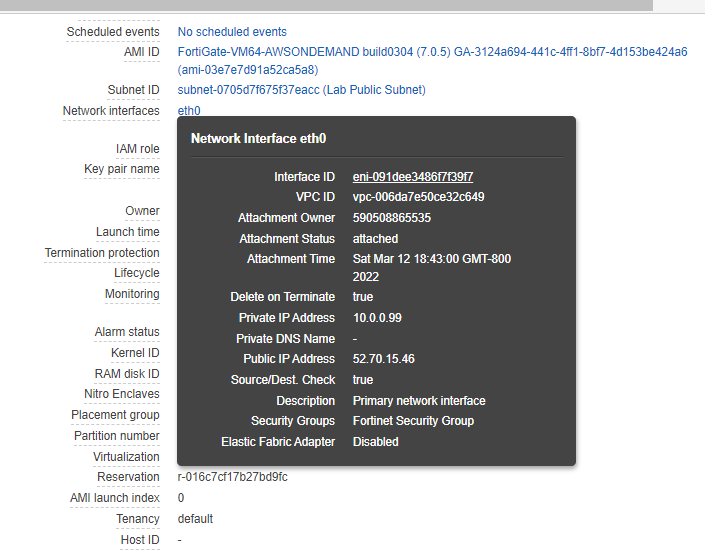
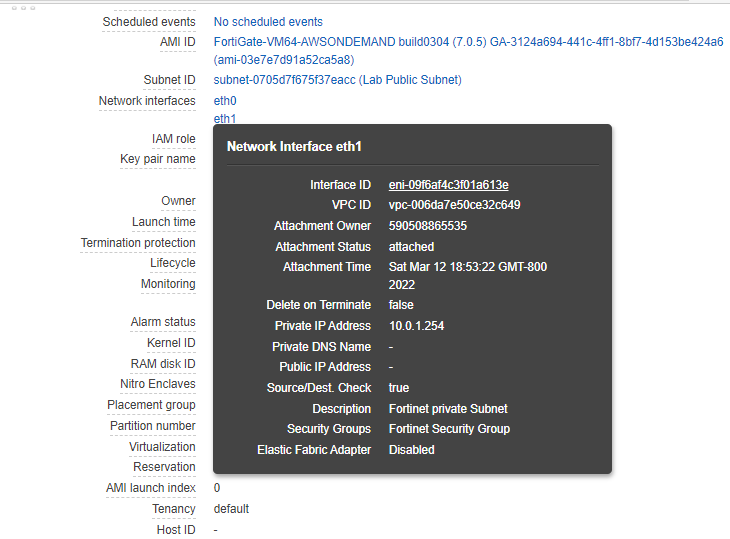
Now, Fortinet has two interfaces. One is Private, and another one is Public.
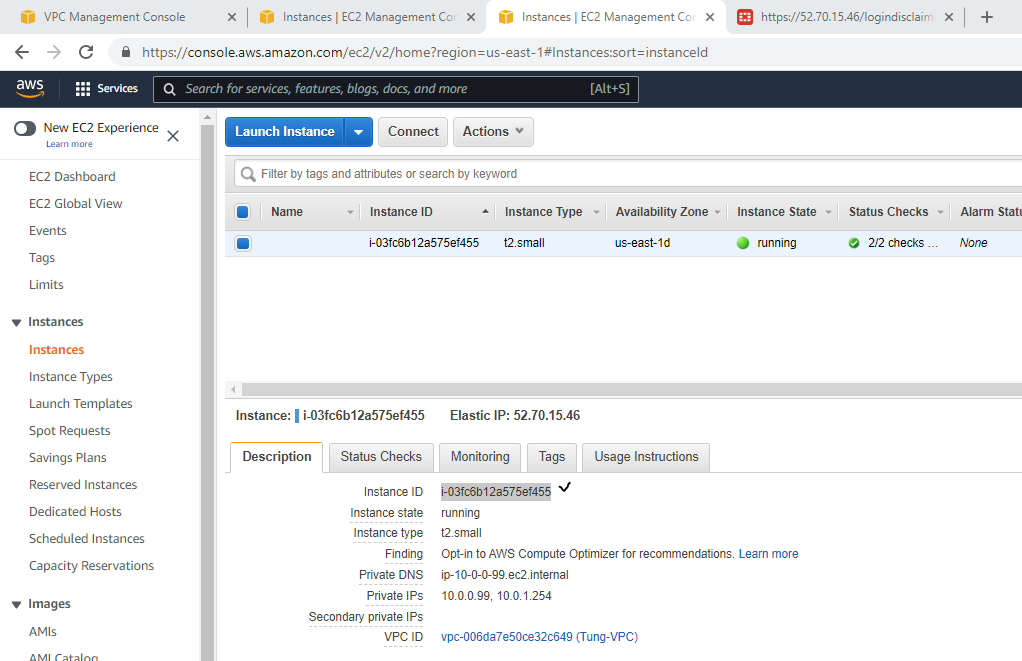
Access Fortinet via the Internet.
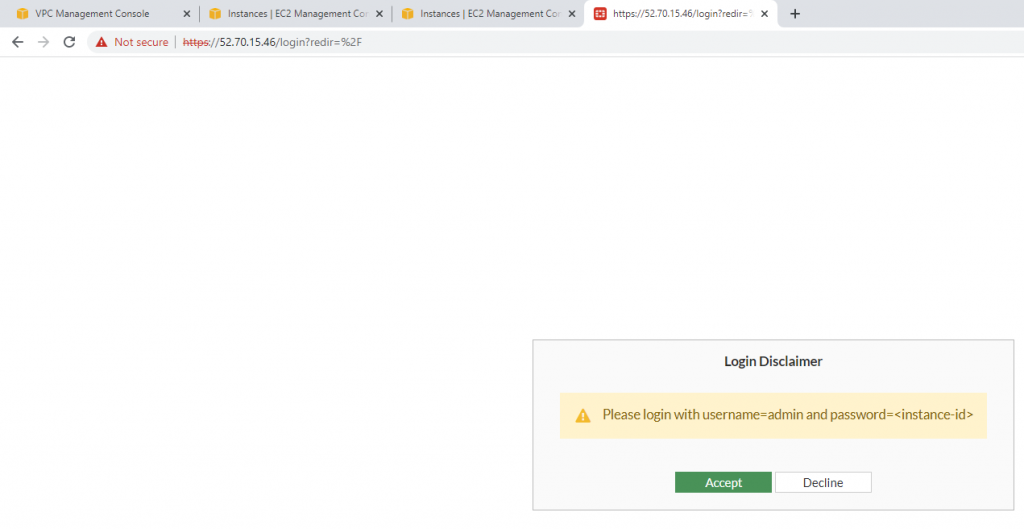
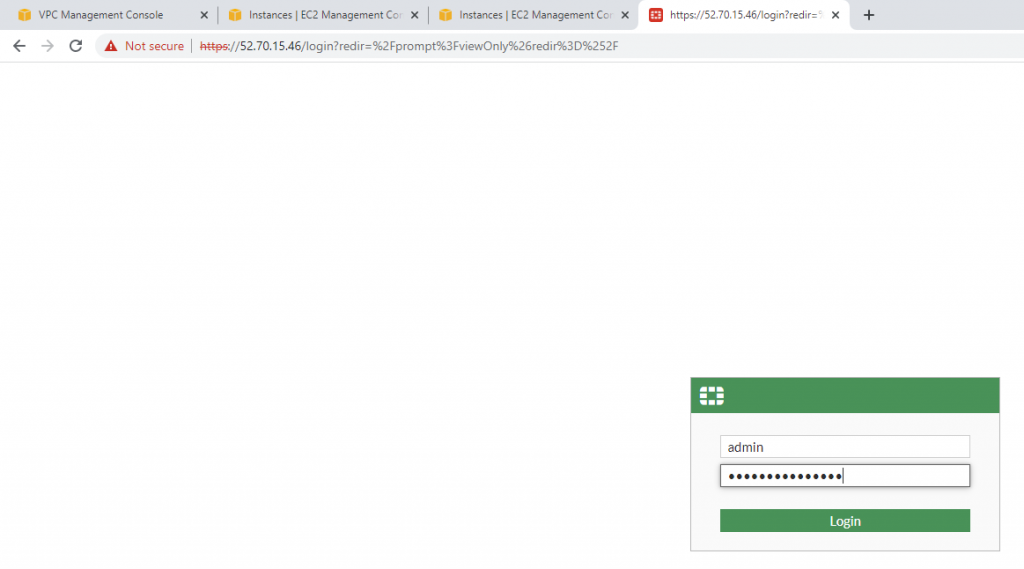
Login to Fortinet.
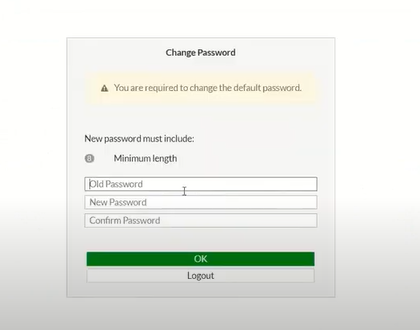
Change password to login to Fortinet.
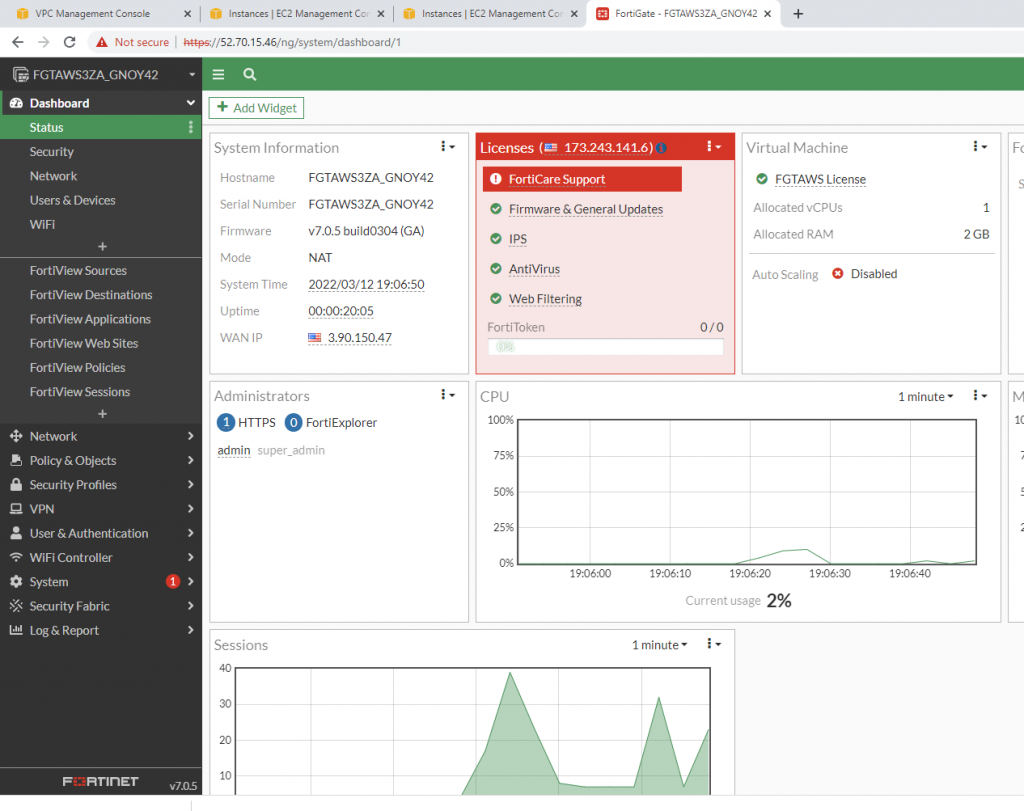
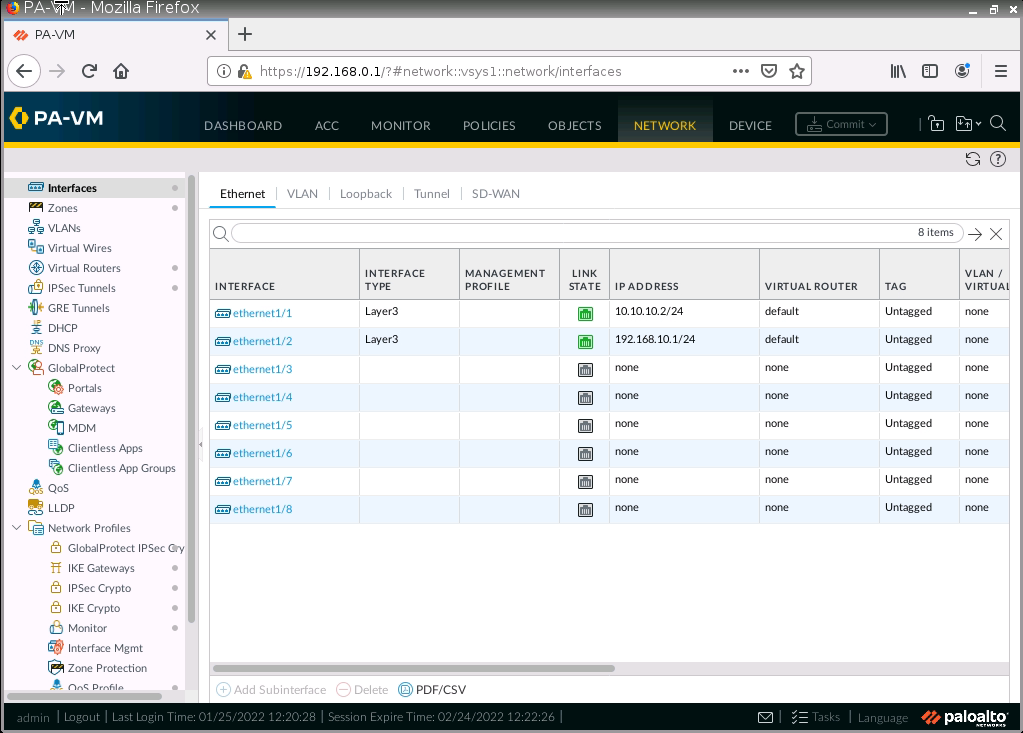
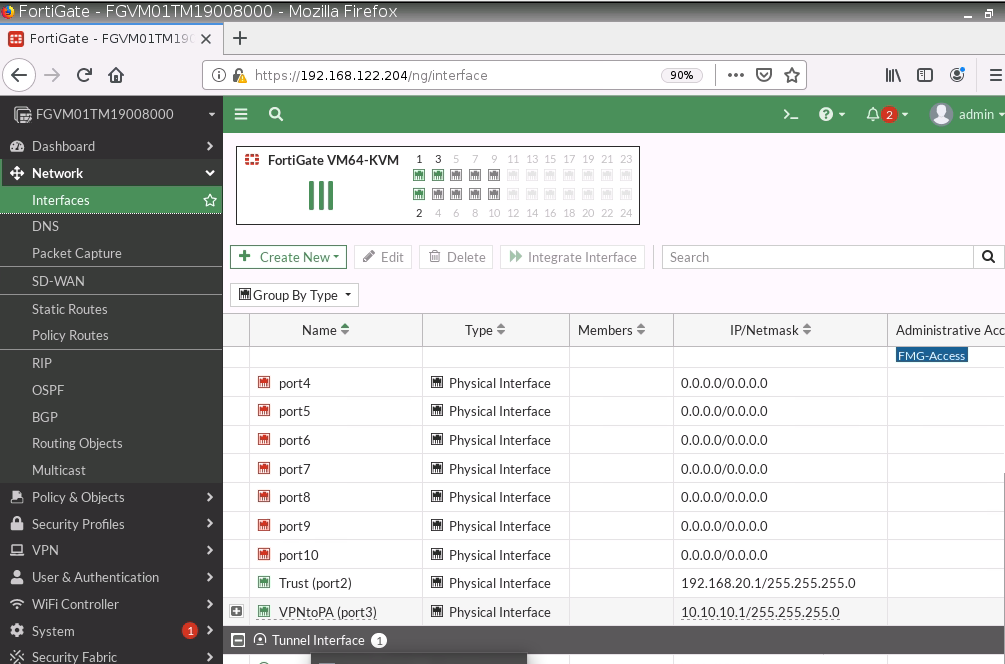
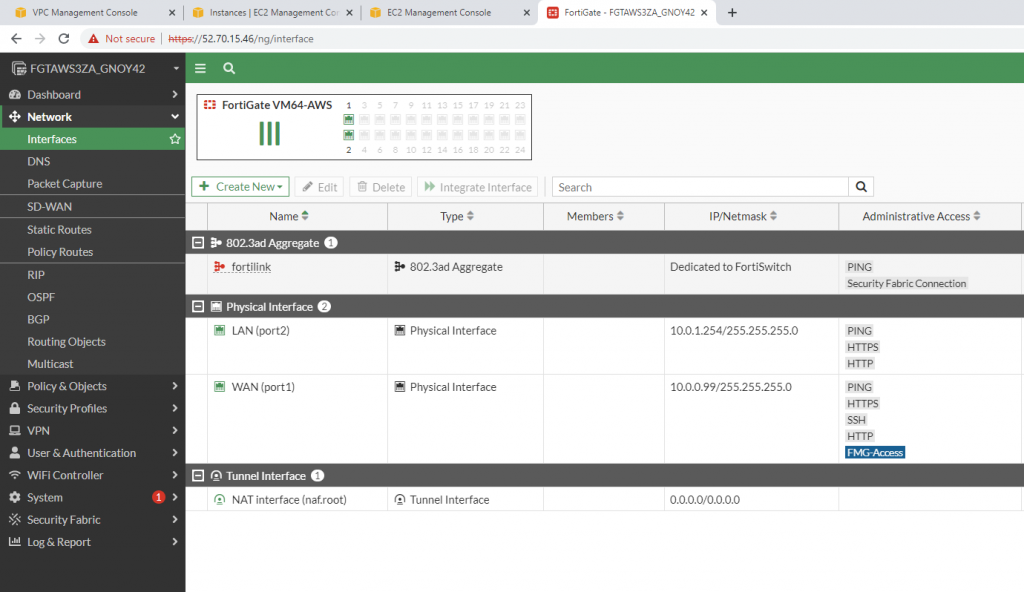
Edit interfaces.
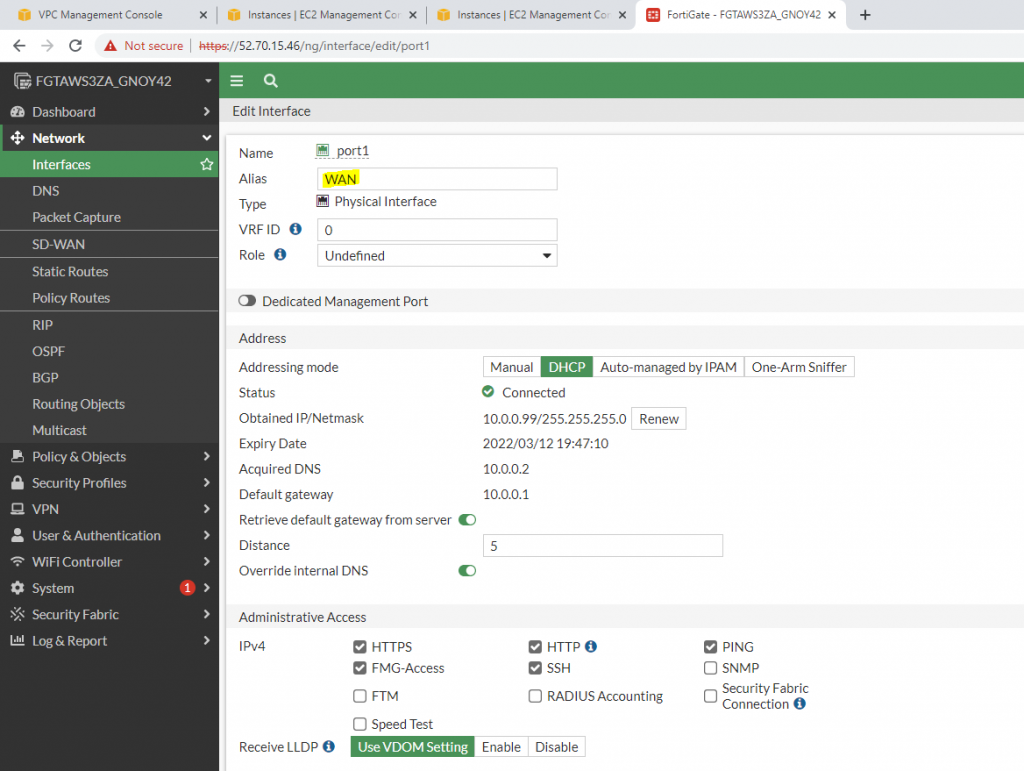
WAN interface.
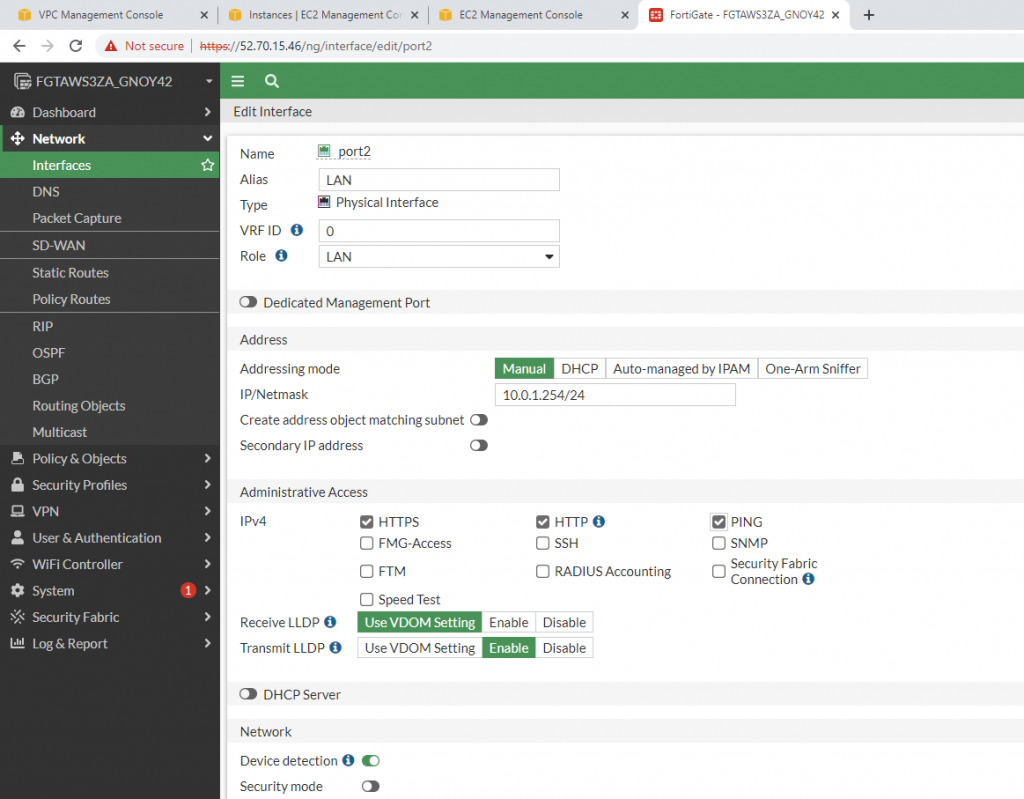
LAN interface.
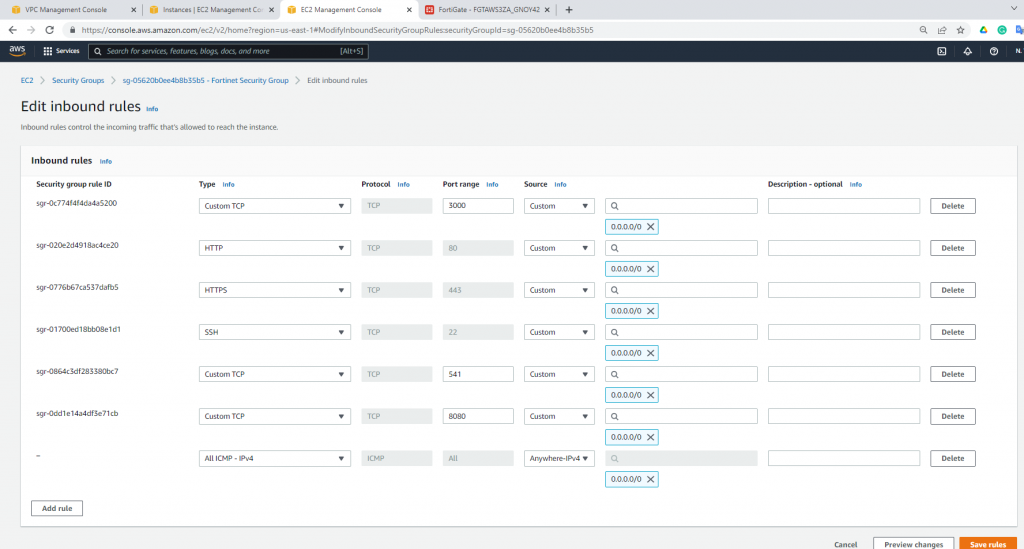
Edit Security Group to allow to ping Fortinet.
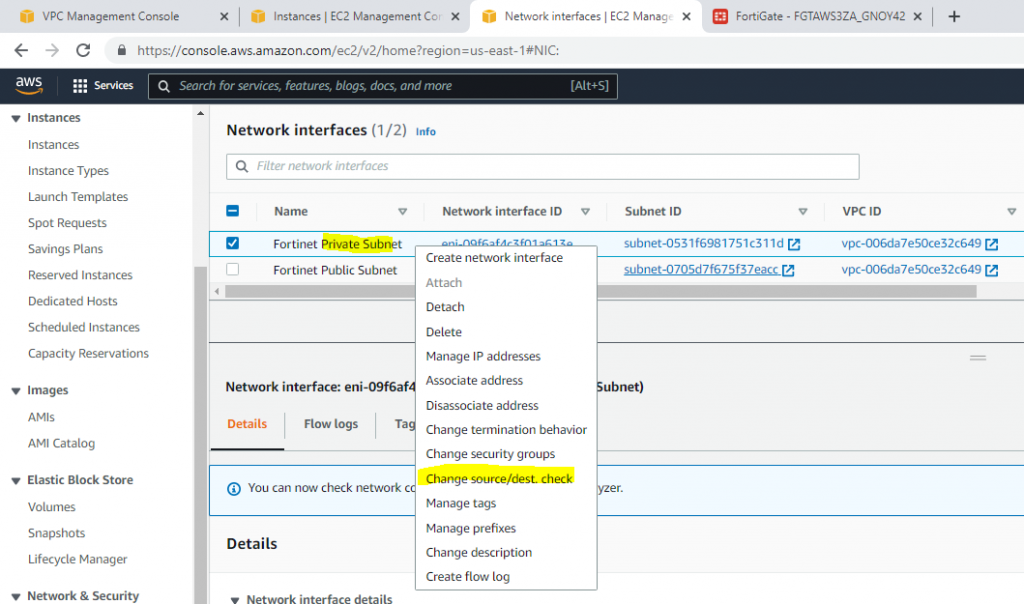
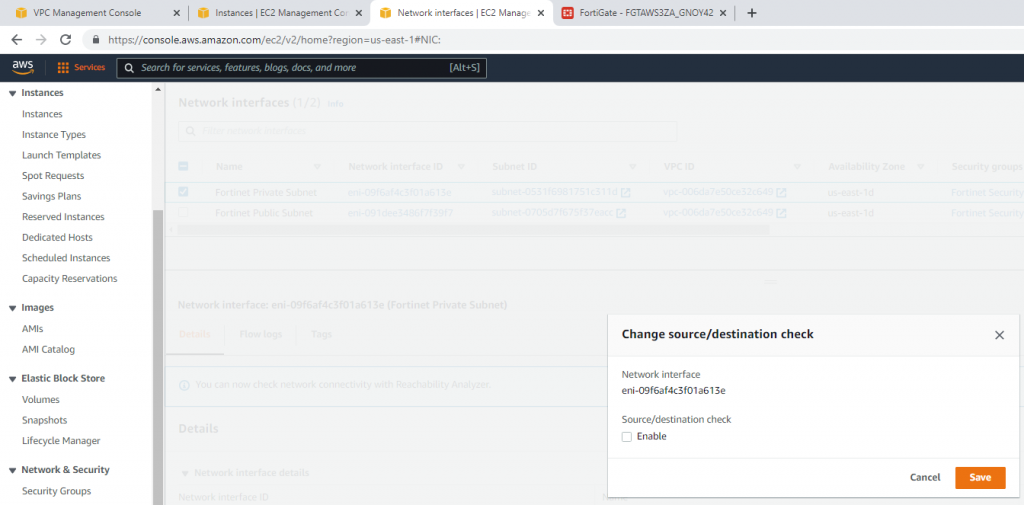
Disable Source and Destination Check on “Fortinet Private subnet”.
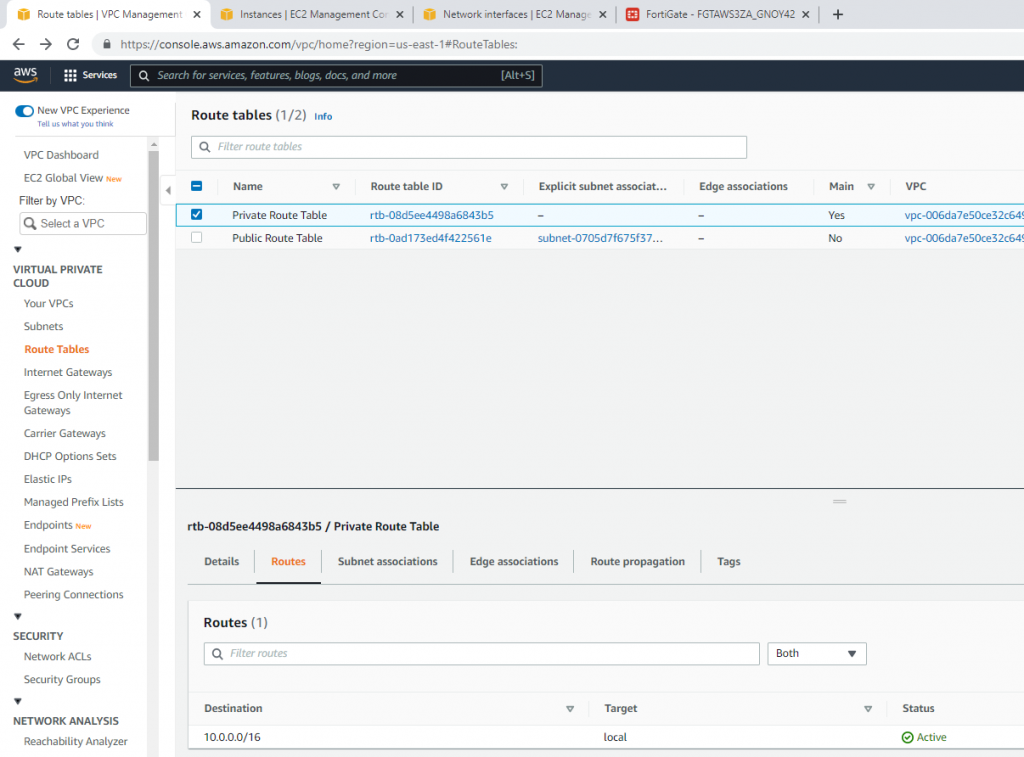
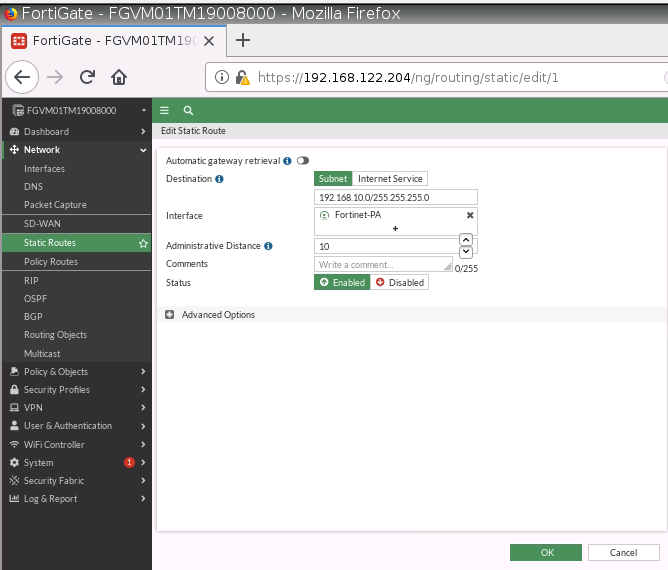
Now, change the route to route private subnet traffic via Fortinet Private subnet interface.
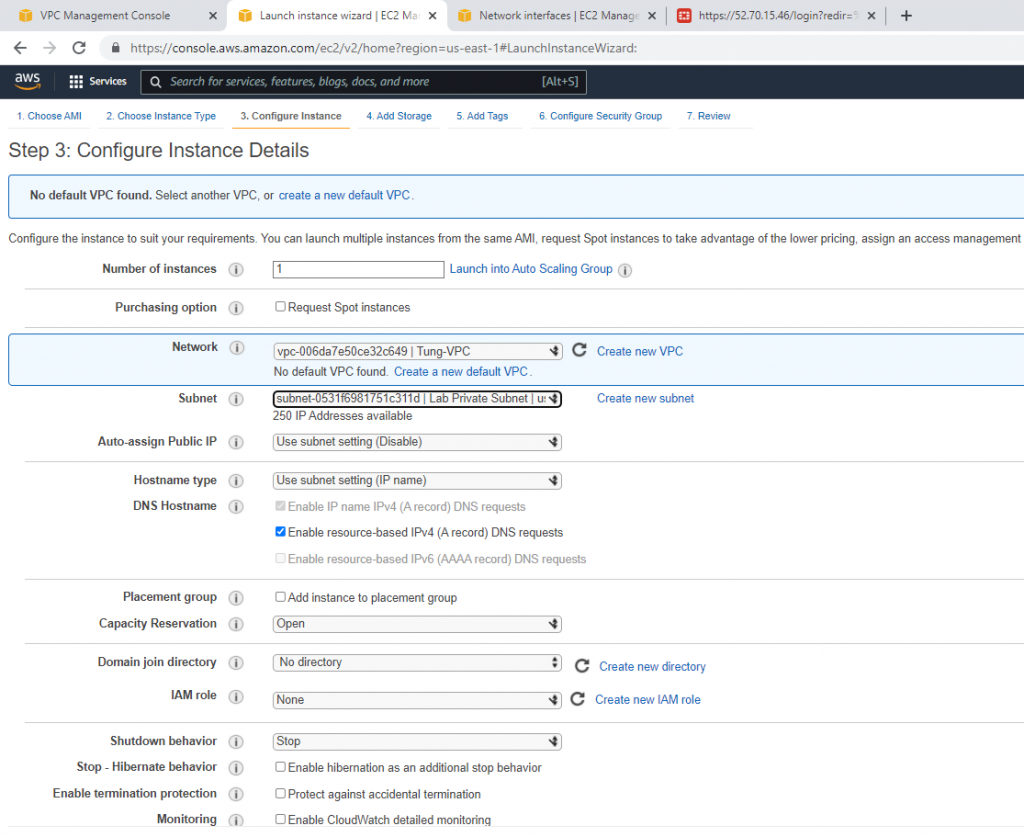
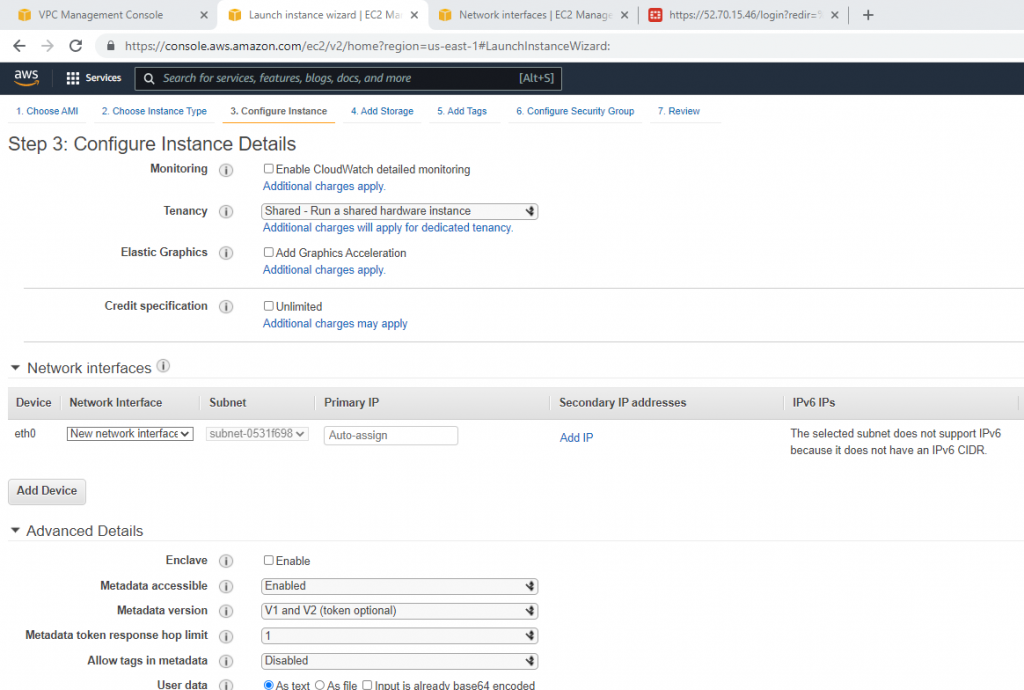
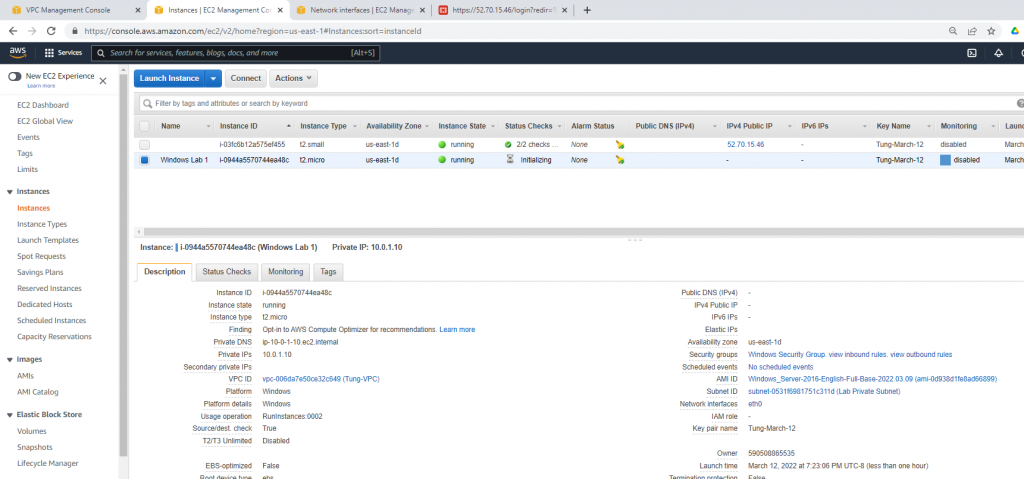
Create a new Windows 2016 VM EC2. The machine is belonged to “Lab private Subnet”.
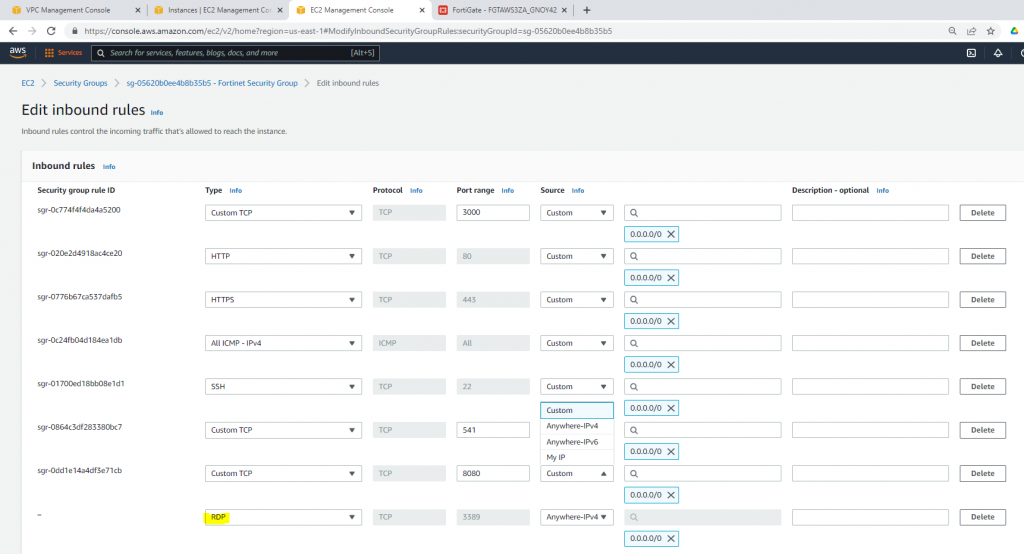
Create a new Windows Security Group to allow HTTP and RDP traffic.
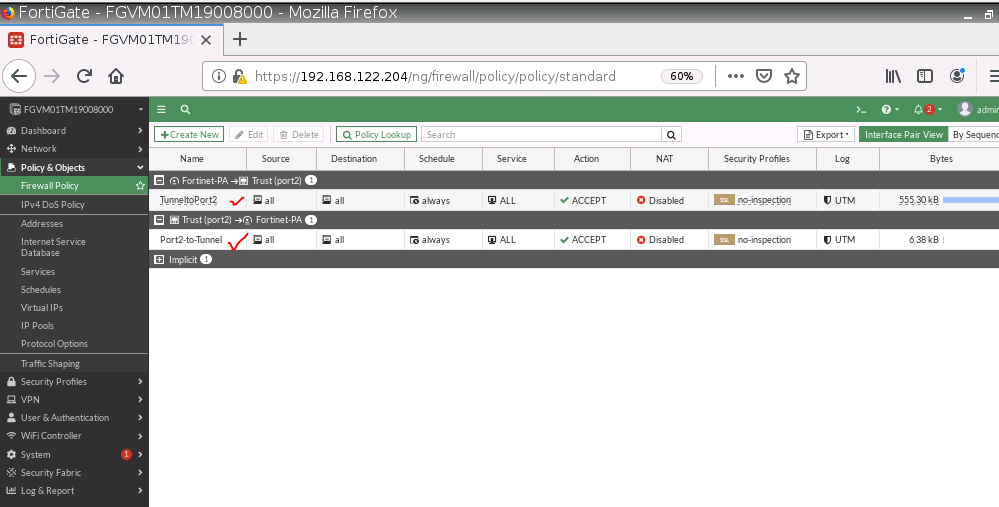
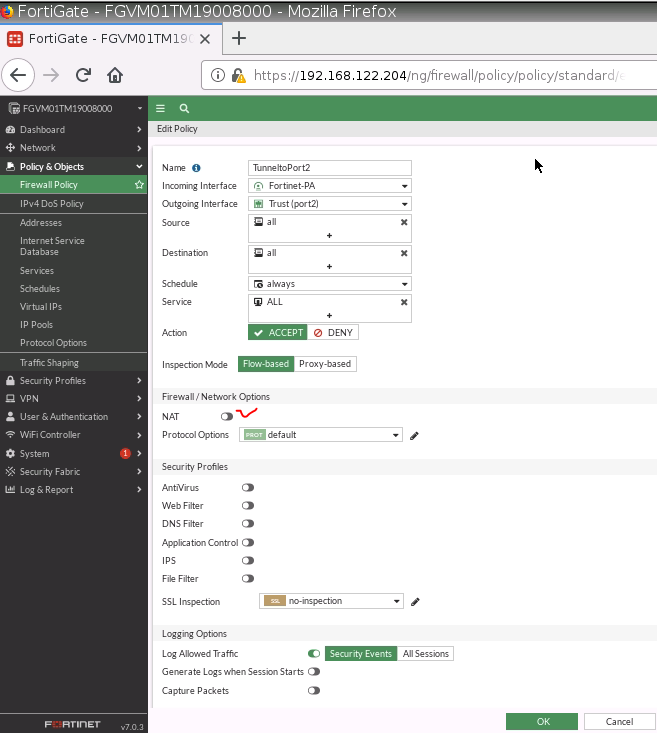
Back to Fortinet to configure FIrewall Policy to allow traffic from Fortinet Private subnet to access the Internet.
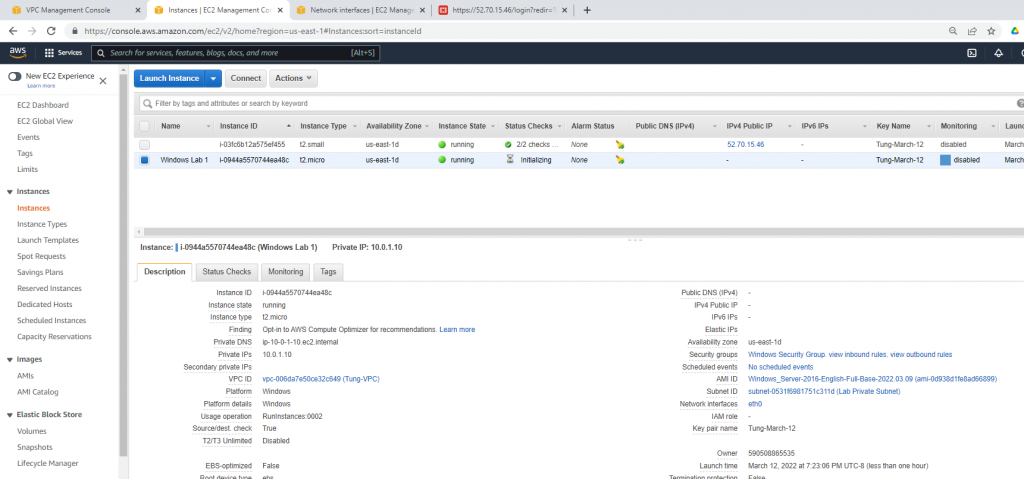
Configure port forwarding to allow traffic.
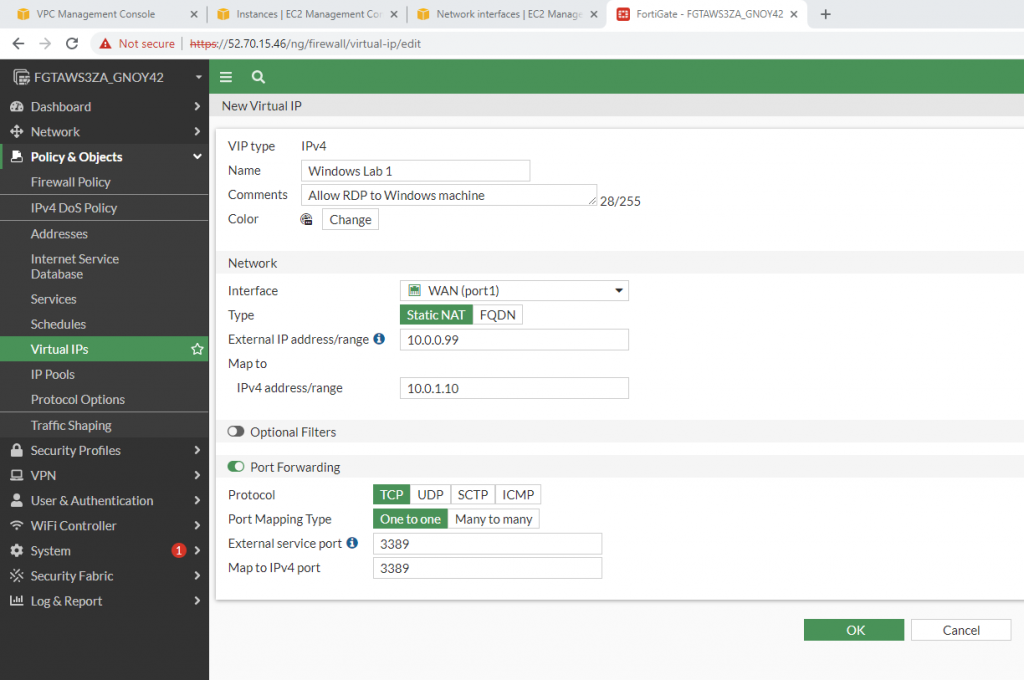
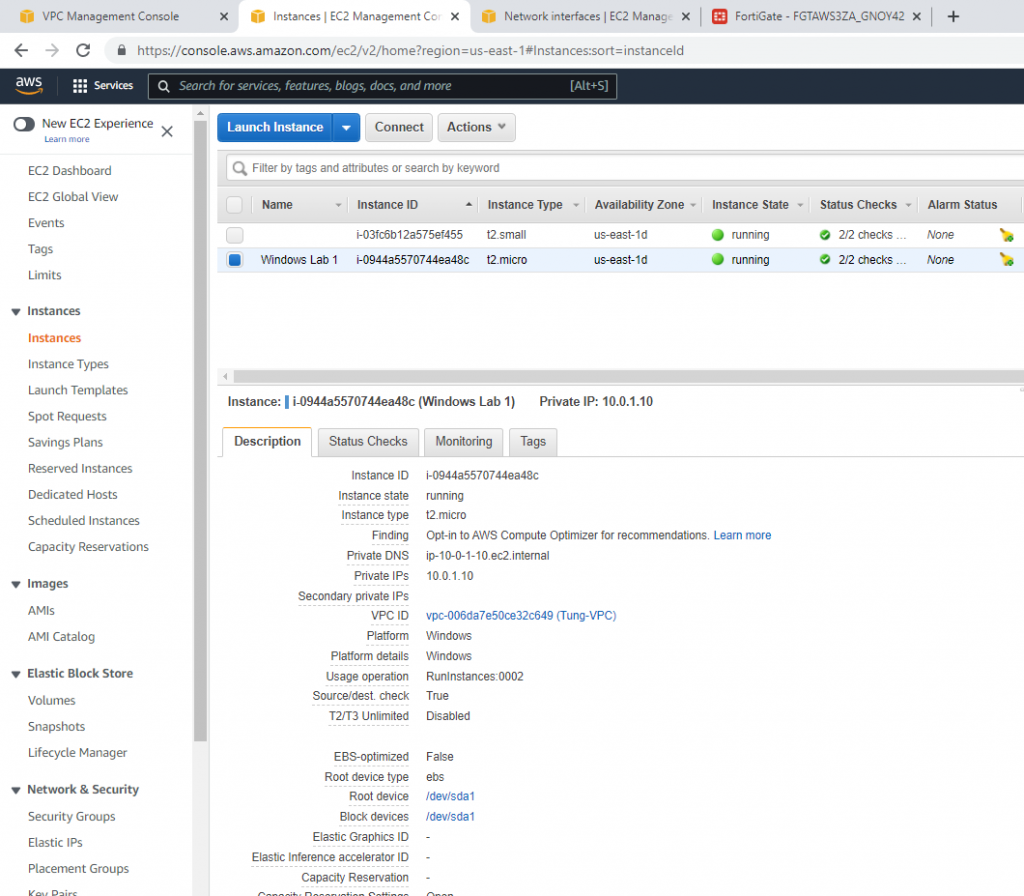
Allow inbound traffic from WAN to this machine.
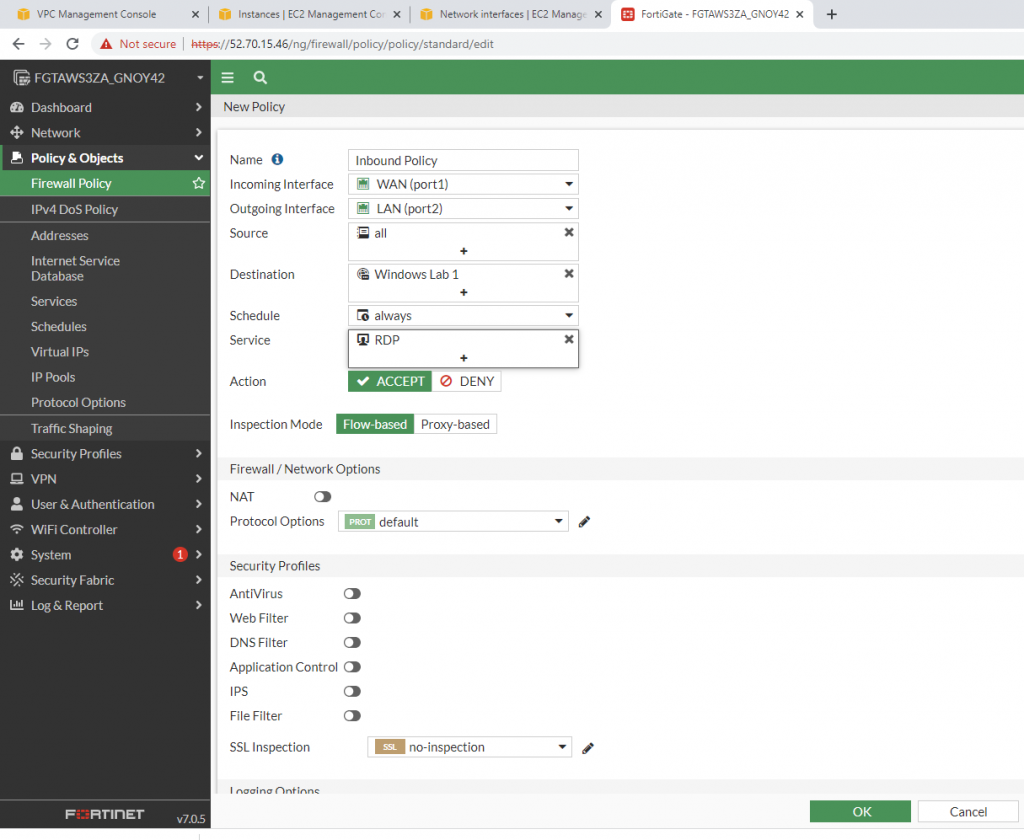
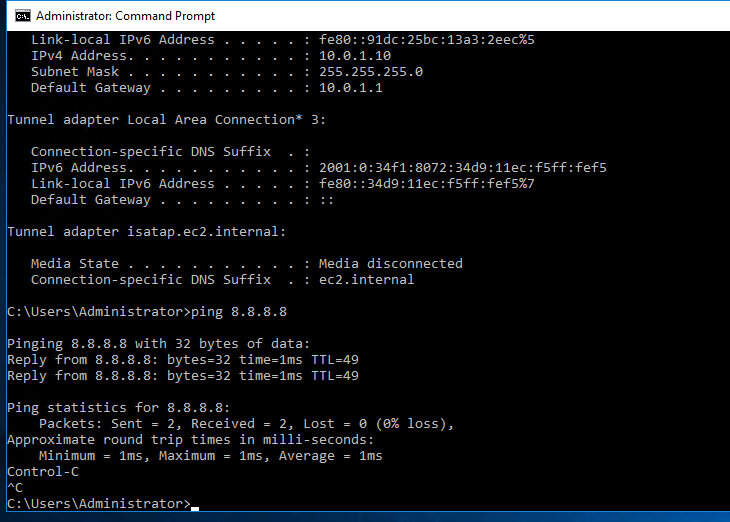
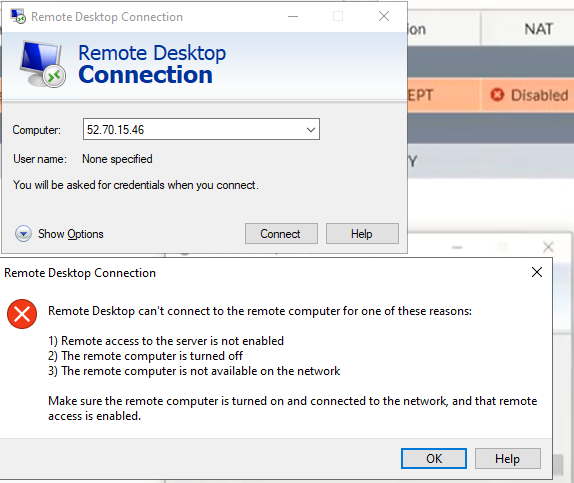
Try to access the machine.
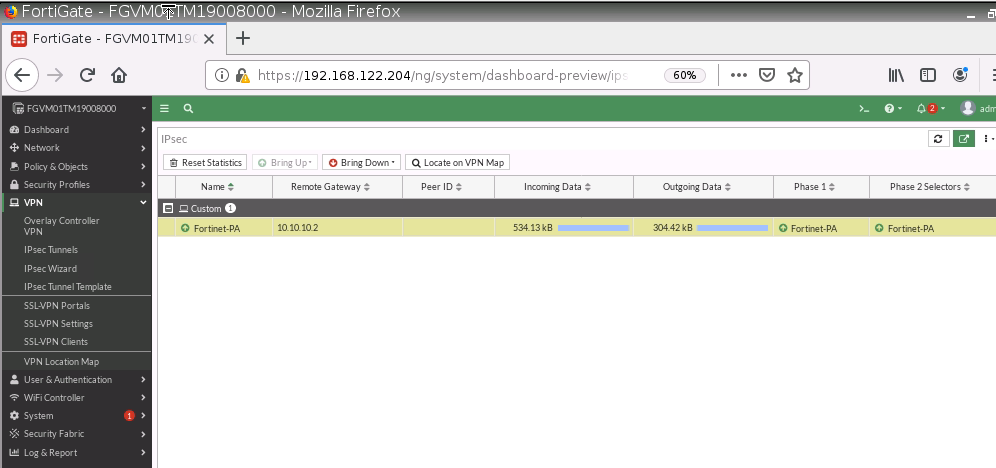
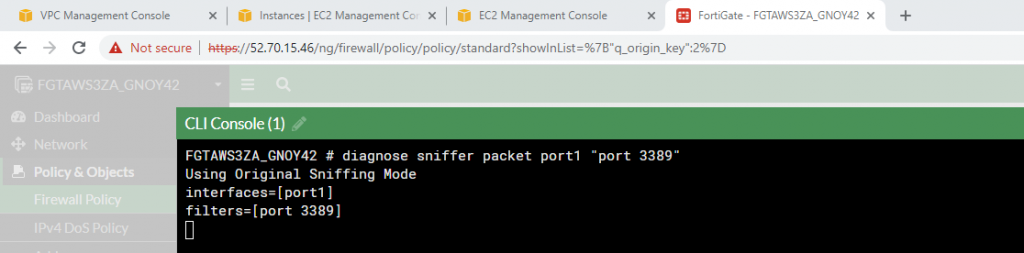
Sniffer traffic on Fortinet.
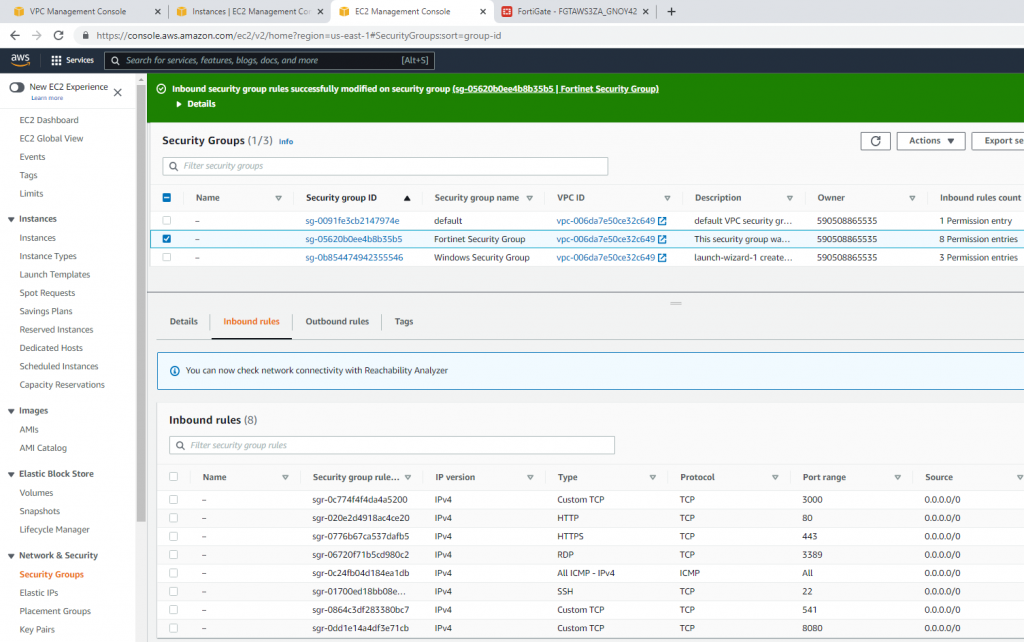
Modify the Security group to allow RDP.
Load private key to decrypt Windows password.
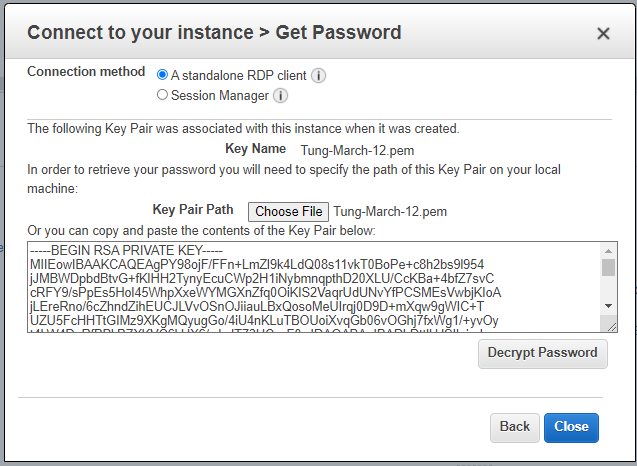
Access RDP to Windows 2016 instance on AWS.
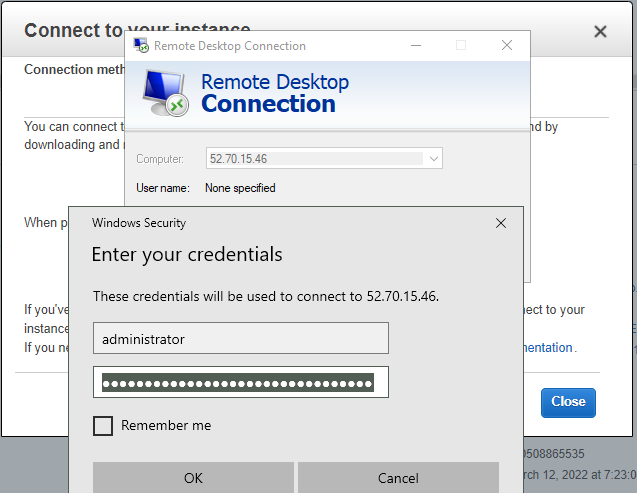
Now we can see the RDP traffic via Fortinet.
diagnose sniffer packet port1 "port 3389"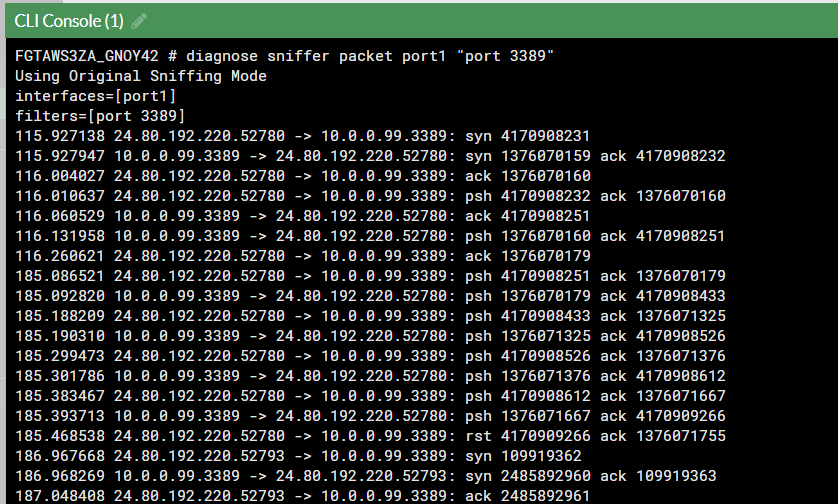
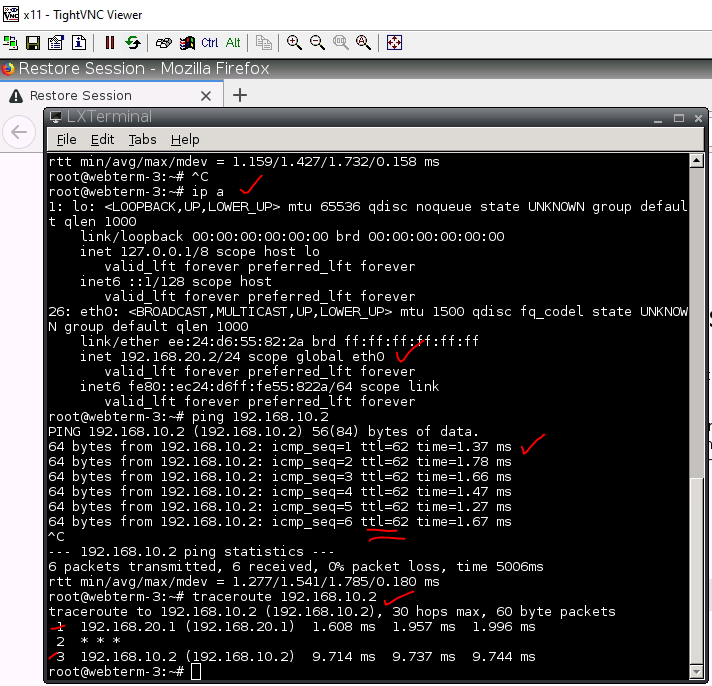
The Windows machine is able to access the Internet.